Microchip MIC45404 Handleiding
Microchip
Niet gecategoriseerd
MIC45404
Lees hieronder de 📖 handleiding in het Nederlandse voor Microchip MIC45404 (34 pagina's) in de categorie Niet gecategoriseerd. Deze handleiding was nuttig voor 22 personen en werd door 2 gebruikers gemiddeld met 4.5 sterren beoordeeld
Pagina 1/34
2015-2017 Microchip Technology Inc. DS20005478B-page 1
MIC45404
Features
• Input Voltage Range: 4.5V to 19V
• Output Current: Up to 5A
• 82% Peak Efficiency at 12 VIN, 0.9 VOUT
• Pin-Selectable Output Voltages: 0.7V, 0.8V, 0.9V,
1.0V, 1.2V, 1.5V, 1.8V, 2.5V, 3.3V
• ±1% Output Voltage Accuracy
• Supports Safe Pre-Biased Start-Up
• Pin-Selectable Current Limit
• Pin-Selectable Switching Frequency
• Internal Soft Start
• Thermal Shutdown
• Hiccup Mode Short-Circuit Protection
• Available in a 54-Lead 6 mm x 10 mm QFN
Package
• Ultra-Low Profile: 2.0 mm Height
• -40°C to +125°C Junction Temperature Range
Applications
• Servers, Data Storage, Routers and Base Stations
• FPGAs, SSD, DSP and Low-Voltage ASIC Power
General Description
The MIC45404 device is an ultra-low profile, synchro-
nous step-down regulator module, featuring a unique
2.0 mm height. The module incorporates a DC-to-DC
regulator, bootstrap capacitor, high-frequency input
capacitor and an inductor in a single package. The
module pinout is optimized to simplify the Printed
Circuit Board (PCB) layout process.
This highly-integrated solution expedites system
design and improves product time to market. The inter-
nal MOSFETs and inductor are optimized to achieve
high efficiency at low output voltage. Due to the fully
optimized design, MIC45404 can deliver up to 5A
current with a wide input voltage range of 4.5V to 19V.
The MIC45404 is available in a 54-lead 6 mm x
10 mm x 2.0 mm QFN package with a junction operat-
ing temperature range from -40C to +125C, which
makes an excellent solution for systems in which PCB
real-estate and height are important limiting factors,
and air flow is restricted.
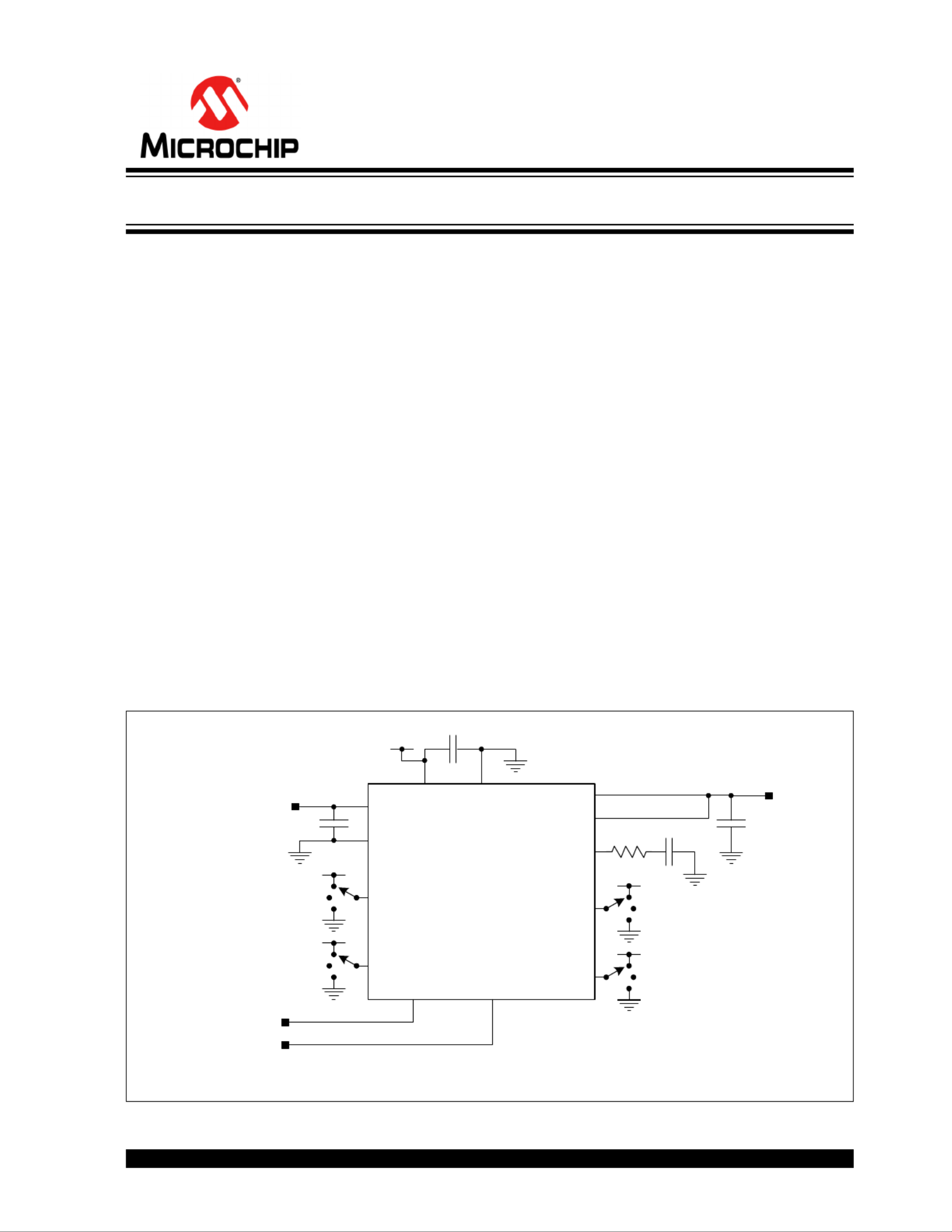
Typical Application
VIN
OUT
VIN
4.5V to 19V
FREQ
VDDA
VOSET1
PG
GND
GND
VOSET0
COMP
EN/DLY
OUTSNS
MIC45404
V
DDA
Power-Good
Enable
VDDA
VDDA
Output
Voltage
Selection
VDDA
Frequency
Selection
ILIM
VDDA
Current Limit
Selection
VOUT
MIC45404 12V 5A DC-to-DC Converter
19V 5A Ultra-Low Profile DC-to-DC Power Module
MIC45404
DS20005478B-page 2 2015-2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
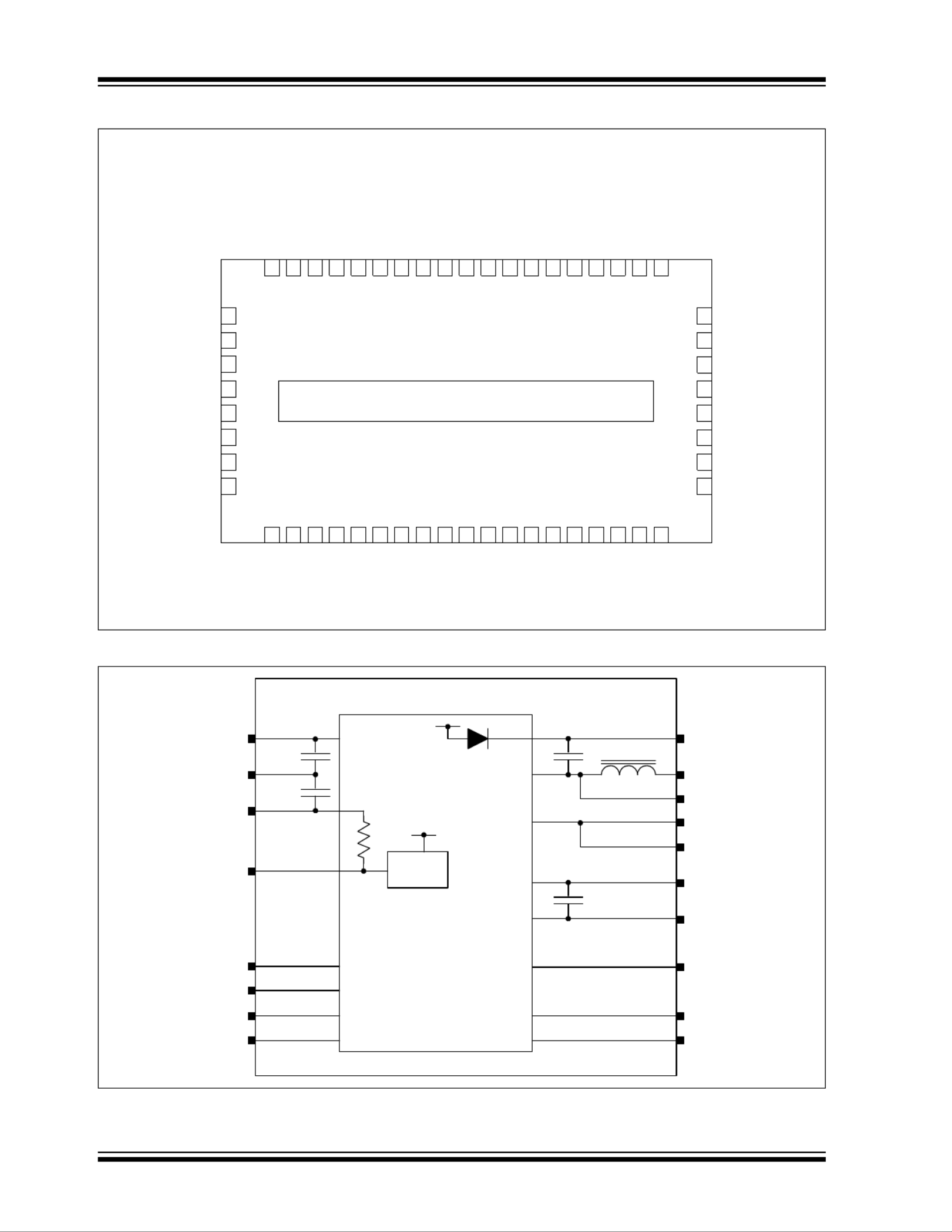
Package Types
Functional Diagram
MIC45404
6 mm x 10 mm QFN*
(Top View)
8
26
22
24
23
3
37
35
34
25
47
46
7
KEEPOUT
GND
GND
BST
PG
VDDA
LX
OUT
GND
21
KEEPOUT
48
38
4
1
2
AGND
VOSET1
NC
41
43
53
OUTSNS
EN/DLY
33
VOSET0
LX
44
45
VDDP
31
30
29
32
52
36
28
20
9
LX
LX
LX
LX
LX
LX
LX
LX
LX
OUT
OUT
12
OUT13
OUT14
OUT15
OUT16
OUT17
OUT18
OUT19
GND
VIN
VIN
27
LX
LX
39
40
LX
KEEPOUT
BST 42
NC
ILIM
49
FREQ
50
51
GND
COMP
54
OUTSNS
KEEPOUT10
OUT11
6 GND_EXT
5 GND_EXT
MIC45404YMP
GND_EP
* Includes Exposed Thermal Pad (EP); see Table 3-1.
LX
BST
ILIM
FREQ
VDDA
VOSET1
PG
AGND
VOSET0
COMP
EN/DLY
OUTSNS
VIN
PGND
VDDP
PWM
Regulator
100 nF
47 pF
LX
BST
VOSET1
AGND
VOSET0
GND_EP
OUTSNS
GND
COMP
OUT
ILIM
FREQ
VDDA
PG
EN/DLY
VIN
VDDP
GND_EXT
VDDP
LDO
VIN
2015-2017 Microchip Technology Inc. DS20005478B-page 3
MIC45404
1.0 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings†
VIN to AGND ................................................................................................................................................ -0.3V to +20V
VDDP
, VDDA to AGND ..................................................................................................................................... -0.3V to +6V
VDDP to VDDA ............................................................................................................................................ -0.3V to +0.3V
VOSETX, FREQ, ILIM, to AGND .................................................................................................................... -0.3V to +6V
BST to LX..................................................................................................................................................... -0.3V to +6V
BST to AGND .............................................................................................................................................. -0.3V to +26V
EN/DLY to AGND...................................................................................................................... -0.3V to V
DDA + 0.3V, +6V
PG to AGND .................................................................................................................................................. -0.3V to +6V
COMP, OUTSNS to A
GND ....................................................................................................... -0.3V to V
DDA + 0.3V, +6V
AGND to GND ............................................................................................................................................ -0.3V to +0.3V
Junction Temperature .......................................................................................................................................... +150°C
Storage Temperature (TS)...................................................................................................................... -65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) ........................................................................................................................ 260°C
ESD Rating
( )1
HBM ........................................................................................................................................................................... 2kV
MM ........................................................................................................................................................................... 150V
CDM....................................................................................................................................................................... 1500V
Note 1: Devices are ESD-sensitive. Handling precautions are recommended. Human body model, 1.5 k in series
with 100 pF.
Operating Ratings( )1
Supply Voltage (VIN) ..................................................................................................................................... 4.5V to 19V
Externally Applied Analog and Drivers Supply Voltage (V
IN = VDDA = VDDP).............................................. 4.5V to 5.5V
Enable Voltage (EN/DLY)............................................................................................................................... 0V to V
DDA
Power Good (PG) Pull-up Voltage (VPU_PG) ................................................................................................ 0V to 5.5V
Output Current ............................................................................................................................................................. 5A
Junction Temperature (TJ) ..................................................................................................................... -40°C to +125°C
Note 1: The device is not ensured to function outside the operating range.
† Notice: Stresses above those listed under “Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is
a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at those or any other conditions above those indicated in
the operational sections of this specification is not intended. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended
periods may affect device reliability.
Product specificaties
| Merk: | Microchip |
| Categorie: | Niet gecategoriseerd |
| Model: | MIC45404 |
Heb je hulp nodig?
Als je hulp nodig hebt met Microchip MIC45404 stel dan hieronder een vraag en andere gebruikers zullen je antwoorden
Handleiding Niet gecategoriseerd Microchip

11 Maart 2025

11 Maart 2025

25 Februari 2025

25 Februari 2025

25 Februari 2025

25 Februari 2025

25 Februari 2025

25 Februari 2025

25 Februari 2025

25 Februari 2025
Handleiding Niet gecategoriseerd
- Niet gecategoriseerd Electrolux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Braun
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bosch
- Niet gecategoriseerd Philips
- Niet gecategoriseerd HP
- Niet gecategoriseerd IKEA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Candy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sony
- Niet gecategoriseerd Samsung
- Niet gecategoriseerd Delonghi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Indesit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xiaomi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Casio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Panasonic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nikon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Epson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brondi
- Niet gecategoriseerd LG
- Niet gecategoriseerd Huawei
- Niet gecategoriseerd Asus
- Niet gecategoriseerd AEG
- Niet gecategoriseerd ATAG
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bauknecht
- Niet gecategoriseerd BEKO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Canon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Daewoo
- Niet gecategoriseerd DeWalt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Etna
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ford
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fysic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Garmin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grundig
- Niet gecategoriseerd Honeywell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Inventum
- Niet gecategoriseerd JVC
- Niet gecategoriseerd JBL
- Niet gecategoriseerd Junkers
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kenwood
- Niet gecategoriseerd Krups
- Niet gecategoriseerd Karcher
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lego
- Niet gecategoriseerd Liebherr
- Niet gecategoriseerd Miele
- Niet gecategoriseerd Motorola
- Niet gecategoriseerd Medion
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nokia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Olympus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Onkyo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pioneer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Quigg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ravensburger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Siemens
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tefal
- Niet gecategoriseerd Toshiba
- Niet gecategoriseerd Unold
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vaillant
- Niet gecategoriseerd Volvo
- Niet gecategoriseerd VTech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Whirlpool
- Niet gecategoriseerd WOLF-Garten
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wiko
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yamaha
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yealink
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zanussi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zibro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hoover
- Niet gecategoriseerd A.O. Smith
- Niet gecategoriseerd A3
- Niet gecategoriseerd A4tech
- Niet gecategoriseerd ABB
- Niet gecategoriseerd ABC Design
- Niet gecategoriseerd Absima
- Niet gecategoriseerd Abus
- Niet gecategoriseerd ACCU-CHEK
- Niet gecategoriseerd Acer
- Niet gecategoriseerd ACME
- Niet gecategoriseerd Acoustic Solutions
- Niet gecategoriseerd Act
- Niet gecategoriseerd Acti
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ade
- Niet gecategoriseerd Adidas
- Niet gecategoriseerd Adler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Adobe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aduro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Advance Acoustic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Adventuridge
- Niet gecategoriseerd AEA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aeris
- Niet gecategoriseerd Afk
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ag Neovo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Agfa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Airlive
- Niet gecategoriseerd Airlux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aiwa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Akai
- Niet gecategoriseerd Akasa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Akg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Al-ko
- Niet gecategoriseerd Albrecht
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alcatel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alcon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alecto
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alesis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alfen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alienware
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aligator
- Niet gecategoriseerd Allibert
- Niet gecategoriseerd Allied Telesis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Allnet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alpen Kreuzer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alphatronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alpina
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alpine
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alto
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aluratek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Amana
- Niet gecategoriseerd Amazfit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Amazon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ambiano
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ambient
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ambrogio
- Niet gecategoriseerd American Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Amfra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Amica
- Niet gecategoriseerd Amiko
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ampeg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Amplicom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Amprobe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Anker
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ansmann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Antec
- Niet gecategoriseerd AOC
- Niet gecategoriseerd AOpen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Apa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Apart
- Niet gecategoriseerd Apc
- Niet gecategoriseerd Apple
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aprilia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aqara
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aquapur
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arcelik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Archos
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arendo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Argon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Argus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ariete
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arris
- Niet gecategoriseerd Artsound
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arturia
- Niet gecategoriseerd AS - Schwabe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Asaklitt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ascom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Asko
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aspen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Asrock
- Niet gecategoriseerd Astralpool
- Niet gecategoriseerd Astro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Atika
- Niet gecategoriseerd Atlantic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Atlas
- Niet gecategoriseerd ATN
- Niet gecategoriseerd ATP
- Niet gecategoriseerd Audio Pro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Audio-Technica
- Niet gecategoriseerd Audiolab
- Niet gecategoriseerd Audioline
- Niet gecategoriseerd Audiovox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Audison
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aukey
- Niet gecategoriseerd Auna
- Niet gecategoriseerd Auriol
- Niet gecategoriseerd Autel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Autotek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Avanti
- Niet gecategoriseerd Avaya
- Niet gecategoriseerd AVM
- Niet gecategoriseerd AVTech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Axa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Axis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Axkid
- Niet gecategoriseerd B-tech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Baby Jogger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Baby Lock
- Niet gecategoriseerd BabyGO
- Niet gecategoriseerd BabyHome
- Niet gecategoriseerd BaByliss
- Niet gecategoriseerd Babymoov
- Niet gecategoriseerd Babyzen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Balance
- Niet gecategoriseerd Balay
- Niet gecategoriseerd Barco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bartscher
- Niet gecategoriseerd Basetech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Batavia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bavaria
- Niet gecategoriseerd Be Cool
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beaba
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beafon
- Niet gecategoriseerd BeamZ
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bebe Confort
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beem
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beha-Amprobe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Behringer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Belgacom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Belkin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bellini
- Niet gecategoriseerd Benning
- Niet gecategoriseerd BenQ
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beper
- Niet gecategoriseerd Berkel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Berker
- Niet gecategoriseerd Berner
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bernina
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bertazzoni
- Niet gecategoriseerd BeSafe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bestron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bestway
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beurer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beyerdynamic
- Niet gecategoriseerd BH Fitness
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bialetti
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bifinett
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bigben
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bikemate
- Niet gecategoriseerd Binatone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bionaire
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bissell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Black Decker
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blade
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blaupunkt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blaze
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blomberg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blue
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bluebird
- Niet gecategoriseerd BlueBuilt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bluesound
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blumfeldt
- Niet gecategoriseerd BMW
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bodum
- Niet gecategoriseerd Body Sculpture
- Niet gecategoriseerd Body Solid
- Niet gecategoriseerd BodyCraft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bomann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Boneco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bopita
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bora
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bose
- Niet gecategoriseerd Boso
- Niet gecategoriseerd Boss
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bowflex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brabantia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brandson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brandt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Braun Phototechnik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bravilor Bonamat
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brennenstuhl
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bresser
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brevi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Breville
- Niet gecategoriseerd BrightSign
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brigmton
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brinno
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brinsea
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brita
- Niet gecategoriseerd Britax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Britax-Romer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brother
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bruder Mannesmann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bruynzeel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bryton
- Niet gecategoriseerd BT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Buffalo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bugaboo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bullet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bunn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Burg-Wachter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Burley
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bushnell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Butler
- Niet gecategoriseerd BWT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Byron
- Niet gecategoriseerd D-Jix
- Niet gecategoriseerd D-Link
- Niet gecategoriseerd Daikin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Daitsu
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dali
- Niet gecategoriseerd Danfoss
- Niet gecategoriseerd DAP Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Datalogic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Davis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Definitive Technology
- Niet gecategoriseerd Defy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dell
- Niet gecategoriseerd DeLock
- Niet gecategoriseerd Delta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Denon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Denver
- Niet gecategoriseerd Devialet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Devolo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Digi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Digitech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Digitus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dimplex
- Niet gecategoriseerd DIO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dirt Devil
- Niet gecategoriseerd DJI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dnt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dobar
- Niet gecategoriseerd DOD
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dolmar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dometic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Domo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Domyos
- Niet gecategoriseerd Doro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dorr
- Niet gecategoriseerd Draytek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Drayton
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dream
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dreamland
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dremel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dual
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dualit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dunlop
- Niet gecategoriseerd Duro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Duromax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Duronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Duux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dymo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dymond
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dyson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Easy Home
- Niet gecategoriseerd Easymaxx
- Niet gecategoriseerd Easypix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eaton
- Niet gecategoriseerd EBERLE
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eberspacher
- Niet gecategoriseerd Echo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Echowell
- Niet gecategoriseerd ECTIVE
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eden
- Niet gecategoriseerd Edesa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Edgestar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Edilkamin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Edimax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Edision
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ednet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Efbe-schott
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eheim
- Niet gecategoriseerd Einhell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eizo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elac
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elektrobock
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elgato
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elica
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elite
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elmo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ematic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Emerio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Emerson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Emga
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eminent
- Niet gecategoriseerd Emmaljunga
- Niet gecategoriseerd Emporia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Emtec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Enders
- Niet gecategoriseerd Enduro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Energizer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Energy Sistem
- Niet gecategoriseerd Engel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Engenius
- Niet gecategoriseerd Entes
- Niet gecategoriseerd Envivo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eonon
- Niet gecategoriseerd EQ-3
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ergobaby
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ernesto
- Niet gecategoriseerd Esperanza
- Niet gecategoriseerd ESX
- Niet gecategoriseerd ESYLUX
- Niet gecategoriseerd ETA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eufab
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eufy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eureka
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eurochron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eurom
- Niet gecategoriseerd EverFocus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Evga
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ewent
- Niet gecategoriseerd EWT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Excalibur
- Niet gecategoriseerd Exit Toys
- Niet gecategoriseerd Expobar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Exquisit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Extech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ezviz
- Niet gecategoriseerd Faber
- Niet gecategoriseerd FABER CASTELL
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fagor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fakir
- Niet gecategoriseerd FALLER
- Niet gecategoriseerd Falmec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fantec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Farberware
- Niet gecategoriseerd Faytech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fein
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fellowes
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fender
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ferguson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ferm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ferroli
- Niet gecategoriseerd Festool
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fiio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fimer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Finder
- Niet gecategoriseerd Finnlo
- Niet gecategoriseerd FireAngel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Firefriend
- Niet gecategoriseerd FireKing
- Niet gecategoriseerd First Alert
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fischer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fisher And Paykel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fisher Paykel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fisher Price
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fiskars
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fissler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fitbit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Flamingo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Flex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Flir
- Niet gecategoriseerd Florabest
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fluke
- Niet gecategoriseerd Focal
- Niet gecategoriseerd Focusrite
- Niet gecategoriseerd FoodSaver
- Niet gecategoriseerd Foppapedretti
- Niet gecategoriseerd Formuler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Foscam
- Niet gecategoriseerd Franke
- Niet gecategoriseerd Franklin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fresh N Rebel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Friedland
- Niet gecategoriseerd Frigidaire
- Niet gecategoriseerd Frilec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fritel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fuji
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fujifilm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fujitsu
- Niet gecategoriseerd Furman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Furuno
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fusion
- Niet gecategoriseerd Futaba
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fuxtec
- Niet gecategoriseerd G3 Ferrari
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gaggenau
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gaggia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Galanz
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gamma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ganz
- Niet gecategoriseerd GAO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Garden Feelings
- Niet gecategoriseerd Garden Lights
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gardena
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gardenline
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gardol
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gastroback
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gastronoma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gazelle
- Niet gecategoriseerd GBC
- Niet gecategoriseerd GE
- Niet gecategoriseerd Geemarc
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gembird
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gemini
- Niet gecategoriseerd Generac
- Niet gecategoriseerd Geneva
- Niet gecategoriseerd Genexis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Genius
- Niet gecategoriseerd Geomag
- Niet gecategoriseerd George Foreman
- Niet gecategoriseerd GeoVision
- Niet gecategoriseerd Germania
- Niet gecategoriseerd Geze
- Niet gecategoriseerd Giardino
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gigabyte
- Niet gecategoriseerd Giordani
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gioteck
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gira
- Niet gecategoriseerd Global
- Niet gecategoriseerd GlobalTronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Globo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gloria
- Niet gecategoriseerd Goclever
- Niet gecategoriseerd Godox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Goliath
- Niet gecategoriseerd Goobay
- Niet gecategoriseerd Google
- Niet gecategoriseerd GoPro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gorenje
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gossen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gossen Metrawatt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gourmetmaxx
- Niet gecategoriseerd GP
- Niet gecategoriseerd GPO
- Niet gecategoriseerd GPX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Graco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Graef
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gram
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grandstream
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grasslin
- Niet gecategoriseerd GRE
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gree
- Niet gecategoriseerd Greenworks
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grixx
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grizzly
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grohe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grothe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ground Zero
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gude
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gutfels
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gymform
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gys
- Niet gecategoriseerd H.Koenig
- Niet gecategoriseerd Habitat
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hager
- Niet gecategoriseerd Haier
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hailo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hama
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hammer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hammond
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hamstra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Handicare
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hansa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hanseatic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hansgrohe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hapro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Harman Kardon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hartan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hartke
- Niet gecategoriseerd Harvia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hasbro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hasselblad
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hauck
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hayward
- Niet gecategoriseerd Heidemann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Helios
- Niet gecategoriseerd Helix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hendi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hercules
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hertz
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hifonics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hikoki
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hikvision
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hirschmann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hisense
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hitachi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hobby
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hohner
- Niet gecategoriseerd Holzmann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Home Easy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Homedics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Homelite
- Niet gecategoriseerd Honda
- Niet gecategoriseerd Honor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Horizon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Horizon Fitness
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hotpoint
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hotpoint-Ariston
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hozelock
- Niet gecategoriseerd HQ
- Niet gecategoriseerd HQ Power
- Niet gecategoriseerd HTC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hugo Muller
- Niet gecategoriseerd Humax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Humminbird
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hunter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Husqvarna
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hyundai
- Niet gecategoriseerd I.safe Mobile
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ibico
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ibm
- Niet gecategoriseerd ICE Watch
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ices
- Niet gecategoriseerd Icom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Icon
- Niet gecategoriseerd ICU
- Niet gecategoriseerd Icy Box
- Niet gecategoriseerd ID-Tech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ideal
- Niet gecategoriseerd Iget
- Niet gecategoriseerd Igloo
- Niet gecategoriseerd IHealth
- Niet gecategoriseerd IHome
- Niet gecategoriseerd Iiyama
- Niet gecategoriseerd ILive
- Niet gecategoriseerd Iluv
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ilve
- Niet gecategoriseerd Imperial
- Niet gecategoriseerd Infinity
- Niet gecategoriseerd InFocus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Inglesina
- Niet gecategoriseerd Innoliving
- Niet gecategoriseerd Innovaphone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Insignia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Inspire
- Niet gecategoriseerd Insta360
- Niet gecategoriseerd Intenso
- Niet gecategoriseerd Intergas
- Niet gecategoriseerd Interlogix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Intermatic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Intermec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Intex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Invacare
- Niet gecategoriseerd Inverto
- Niet gecategoriseerd Iomega
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ion
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ipevo
- Niet gecategoriseerd IQAir
- Niet gecategoriseerd IRIS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Irobot
- Niet gecategoriseerd Iseki
- Niet gecategoriseerd Itho
- Niet gecategoriseerd Itho-Daalderop
- Niet gecategoriseerd IVT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kalorik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kambrook
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kathrein
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kayser
- Niet gecategoriseerd KEF
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kelvinator
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kenko
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kenmore
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kensington
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kerbl
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kern
- Niet gecategoriseerd Keter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ketron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Keurig
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kicker
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kisag
- Niet gecategoriseerd KitchenAid
- Niet gecategoriseerd Klarfit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Klarstein
- Niet gecategoriseerd KlikaanKlikuit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Klipsch
- Niet gecategoriseerd Knog
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kodak
- Niet gecategoriseerd Koenic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Koenig
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kogan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kohler
- Niet gecategoriseerd KONFTEL
- Niet gecategoriseerd Konica Minolta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Konig
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kopp
- Niet gecategoriseerd Korg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Korona
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kress
- Niet gecategoriseerd Krontaler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kruidvat
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kubota
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kupper
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kuppersbusch
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kyocera
- Niet gecategoriseerd LaCie
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lagrange
- Niet gecategoriseerd Laica
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lamax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lanaform
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lancom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Landmann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lanzar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Laser
- Niet gecategoriseerd Laserliner
- Niet gecategoriseerd Laurastar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lava
- Niet gecategoriseerd LD Systems
- Niet gecategoriseerd Legamaster
- Niet gecategoriseerd Leica
- Niet gecategoriseerd Leifheit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Leitz
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lenco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lenovo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Leotec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lervia
- Niet gecategoriseerd LevelOne
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lexibook
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lexmark
- Niet gecategoriseerd Life Fitness
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lifespan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Liftmaster
- Niet gecategoriseerd LightZone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Line 6
- Niet gecategoriseerd Linksys
- Niet gecategoriseerd Little Tikes
- Niet gecategoriseerd Livarno
- Niet gecategoriseerd Livington
- Niet gecategoriseerd Livoo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Loewe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lofrans
- Niet gecategoriseerd Logicom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Logik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Logilink
- Niet gecategoriseerd Logitech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lorelli
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lorex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lotus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lowrance
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lumag
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lupilu
- Niet gecategoriseerd Luvion
- Niet gecategoriseerd Luxman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Luxor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lynx
- Niet gecategoriseerd M-Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mac Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mackie
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maclaren
- Niet gecategoriseerd Macrom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maestro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Magic Care
- Niet gecategoriseerd Magic Chef
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maginon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Magma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Magnat
- Niet gecategoriseerd Magnavox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Makita
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maktec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mamiya
- Niet gecategoriseerd Manhattan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Manitowoc
- Niet gecategoriseerd Manta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Marantz
- Niet gecategoriseerd Marklin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Marmitek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Marquant
- Niet gecategoriseerd Marshall
- Niet gecategoriseerd Martin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Master
- Niet gecategoriseerd Master Lock
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mattel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Max
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maxcom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maxdata
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maxell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maxi-Cosi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maxicool
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maximum
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maxview
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maxwell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maxxmee
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maxxter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maytag
- Niet gecategoriseerd MB Quart
- Niet gecategoriseerd McCulloch
- Niet gecategoriseerd Meade
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mebus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Medela
- Niet gecategoriseerd Medeli
- Niet gecategoriseerd Media-tech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Medisana
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mega
- Niet gecategoriseerd Megableu
- Niet gecategoriseerd Megasat
- Niet gecategoriseerd Megger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Meireles
- Niet gecategoriseerd Melinera
- Niet gecategoriseerd Melissa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Melitta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Meradiso
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mercury
- Niet gecategoriseerd Meridian
- Niet gecategoriseerd Merlin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mesko
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mestic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Metabo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Metrel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Metrix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Metronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Metz
- Niet gecategoriseerd Michelin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Microlife
- Niet gecategoriseerd Microsoft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Midea
- Niet gecategoriseerd Midland
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mikrotik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Milwaukee
- Niet gecategoriseerd Minix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Minolta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Minox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Miomare
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mistral
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mitsubishi
- Niet gecategoriseerd MJX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mobicool
- Niet gecategoriseerd Monacor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Monitor Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mophie
- Niet gecategoriseerd Morphy Richards
- Niet gecategoriseerd Moulinex
- Niet gecategoriseerd MPM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mr Coffee
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mr Gardener
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mr Handsfree
- Niet gecategoriseerd MSI
- Niet gecategoriseerd MSpa
- Niet gecategoriseerd MTD
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mtx Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mulex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Muller
- Niet gecategoriseerd Muse
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mx Onda
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nabo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nacon
- Niet gecategoriseerd NAD
- Niet gecategoriseerd Naim
- Niet gecategoriseerd Napoleon
- Niet gecategoriseerd National Geographic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nautilus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Navionics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Navitel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Navman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nebula
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nedis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Neewer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Neff
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nemef
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nero
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nest
- Niet gecategoriseerd Netgear
- Niet gecategoriseerd Netis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nevadent
- Niet gecategoriseerd New Pol
- Niet gecategoriseerd Newstar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nextbase
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nibe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nikkei
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nilfisk
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ninja
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nintendo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nivona
- Niet gecategoriseerd Njoy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nobo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Noma
- Niet gecategoriseerd NordicTrack
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nostalgia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Novation
- Niet gecategoriseerd Novis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Novy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Noxon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nuance
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nubert
- Niet gecategoriseerd Numatic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nuna
- Niet gecategoriseerd NutriBullet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nvidia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pabobo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Paladin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Palm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Palson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Paradigm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Parkside
- Niet gecategoriseerd Parrot
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pattfield
- Niet gecategoriseerd Patton
- Niet gecategoriseerd PCE
- Niet gecategoriseerd PCE Instruments
- Niet gecategoriseerd Peavey
- Niet gecategoriseerd Peerless
- Niet gecategoriseerd Peg Perego
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pelgrim
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pentax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Perel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Petsafe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Peugeot
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pfaff
- Niet gecategoriseerd Philco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Phoenix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Phoenix Gold
- Niet gecategoriseerd Phonak
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pieps
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pinolino
- Niet gecategoriseerd PKM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Plantiflor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Plantronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Platinet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Playmobil
- Niet gecategoriseerd Playtive
- Niet gecategoriseerd Plugwise
- Niet gecategoriseerd Plustek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pointer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Polar
- Niet gecategoriseerd POLARIS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Polaroid
- Niet gecategoriseerd Polk
- Niet gecategoriseerd Polti
- Niet gecategoriseerd Power Dynamics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Powerfix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Powerplus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Praktica
- Niet gecategoriseerd Prem-i-air
- Niet gecategoriseerd Premier
- Niet gecategoriseerd Prenatal
- Niet gecategoriseerd President
- Niet gecategoriseerd Prestigio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Primera
- Niet gecategoriseerd Primo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Princess
- Niet gecategoriseerd Privileg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pro-User
- Niet gecategoriseerd ProfiCook
- Niet gecategoriseerd Profile
- Niet gecategoriseerd Profizelt24
- Niet gecategoriseerd Profoon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Progress
- Niet gecategoriseerd Proline
- Niet gecategoriseerd Protector
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pulsar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pure
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pyle
- Niet gecategoriseerd Python
- Niet gecategoriseerd Q Acoustics
- Niet gecategoriseerd QNAP
- Niet gecategoriseerd Quantum
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rademacher
- Niet gecategoriseerd Radiant
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rainbow
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ranex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rangemaster
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ravelli
- Niet gecategoriseerd Raymarine
- Niet gecategoriseerd Razer
- Niet gecategoriseerd RCA
- Niet gecategoriseerd RCF
- Niet gecategoriseerd Realme
- Niet gecategoriseerd Recaro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Redmond
- Niet gecategoriseerd Reebok
- Niet gecategoriseerd Reer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Reflecta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Reflexion
- Niet gecategoriseerd Reich
- Niet gecategoriseerd REL Acoustics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Reloop
- Niet gecategoriseerd Remington
- Niet gecategoriseerd REMKO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Renegade
- Niet gecategoriseerd Renkforce
- Niet gecategoriseerd REVITIVE
- Niet gecategoriseerd Revlon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Revo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Revox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ricoh
- Niet gecategoriseerd Riello
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ring
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rittal
- Niet gecategoriseerd Roadstar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Robust
- Niet gecategoriseerd Roccat
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rockford Fosgate
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rocktrail
- Niet gecategoriseerd Roland
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rollei
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rommelsbacher
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rosieres
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rossmax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rotel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rowenta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Roxio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Royal Sovereign
- Niet gecategoriseerd RugGear
- Niet gecategoriseerd Russell Hobbs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ryobi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sabo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Safety 1st
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sage
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sagem
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sagemcom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Saitek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Salora
- Niet gecategoriseerd Salta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Salter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Salton
- Niet gecategoriseerd Salus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Samlex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Samson
- Niet gecategoriseerd SanDisk
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sangean
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sanitas
- Niet gecategoriseerd Santos
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sanus Systems
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sanwa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sanyo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Saramonic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Saro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Satel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Saturn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sauber
- Niet gecategoriseerd Scala
- Niet gecategoriseerd Scancool
- Niet gecategoriseerd Scandomestic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schaudt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Scheppach
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schneider
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schwinn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Scott
- Niet gecategoriseerd Seagate
- Niet gecategoriseerd SeaLife
- Niet gecategoriseerd SEB
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sebo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Seecode
- Niet gecategoriseerd Segway
- Niet gecategoriseerd Seiko
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sekonic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Selfsat
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sena
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sencor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sencys
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sennheiser
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sensiplast
- Niet gecategoriseerd Severin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Shark
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sharkoon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sharp
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sharper Image
- Niet gecategoriseerd Shimano
- Niet gecategoriseerd Shindaiwa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Shoprider
- Niet gecategoriseerd Showtec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Siedle
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sigma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Silkn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Silva
- Niet gecategoriseerd Silvercrest
- Niet gecategoriseerd Silverline
- Niet gecategoriseerd Simeo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Simpark
- Niet gecategoriseerd Simrad
- Niet gecategoriseerd Singer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sirius
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sitecom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Skil
- Niet gecategoriseerd Skullcandy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Skymaster
- Niet gecategoriseerd SMA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Smart
- Niet gecategoriseerd Smartwares
- Niet gecategoriseerd SMC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Smeg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Snom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sodastream
- Niet gecategoriseerd Soehnle
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sogo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Solac
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sole Fitness
- Niet gecategoriseerd Solis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Solo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Somfy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sommer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sonos
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sonuus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Soundcraft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Soundmaster
- Niet gecategoriseerd Soundstream
- Niet gecategoriseerd Spektrum
- Niet gecategoriseerd SPT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Spypoint
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stabo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stadler Form
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stamina
- Niet gecategoriseerd Standard Horizon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stanley
- Niet gecategoriseerd Starlyf
- Niet gecategoriseerd Steba
- Niet gecategoriseerd Steelseries
- Niet gecategoriseerd Steinberg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Steinel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stiebel Eltron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stiga
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stihl
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stinger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stirling
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stokke
- Niet gecategoriseerd Strong
- Niet gecategoriseerd Subaru
- Niet gecategoriseerd Suevia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sunbeam
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sunny
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sunpentown
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sunstech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Suntec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Superrollo
- Niet gecategoriseerd SuperTooth
- Niet gecategoriseerd Suunto
- Niet gecategoriseerd Suzuki
- Niet gecategoriseerd Swan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sweex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Swissvoice
- Niet gecategoriseerd Switel
- Niet gecategoriseerd SXT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sylvania
- Niet gecategoriseerd Syma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Synology
- Niet gecategoriseerd TacTic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tamiya
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tamron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tanaka
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tanita
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tannoy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Targus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tascam
- Niet gecategoriseerd Taurus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Taylor
- Niet gecategoriseerd TC Helicon
- Niet gecategoriseerd TCL
- Niet gecategoriseerd Teac
- Niet gecategoriseerd Team
- Niet gecategoriseerd Technaxx
- Niet gecategoriseerd Technicolor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Technics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Technika
- Niet gecategoriseerd Technisat
- Niet gecategoriseerd Techno Line
- Niet gecategoriseerd Technoline
- Niet gecategoriseerd Teka
- Niet gecategoriseerd Telefunken
- Niet gecategoriseerd Telestar
- Niet gecategoriseerd TELEX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Telstra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Teltonika
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tenda
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tepro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Termozeta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Terraillon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Terratec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tesla
- Niet gecategoriseerd Teufel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tevion
- Niet gecategoriseerd Texas
- Niet gecategoriseerd Texas Instruments
- Niet gecategoriseerd TFA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Theben
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thermador
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thermor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thetford
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thinkware
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thomas
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thomson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thorens
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thrustmaster
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thule
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tiger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tiptel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Toa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tommee Tippee
- Niet gecategoriseerd TomTom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Toolcraft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Toolland
- Niet gecategoriseerd Toorx
- Niet gecategoriseerd Topcraft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tork
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tormatic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Toro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tower
- Niet gecategoriseerd Toyotomi
- Niet gecategoriseerd TP Link
- Niet gecategoriseerd Transcend
- Niet gecategoriseerd TranzX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trebs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trekstor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trendnet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Triax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trigano
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tristar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Triton
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trixie
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trotec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Troy-Bilt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Truelife
- Niet gecategoriseerd Truma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trust
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tunturi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Turmix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tusa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Twisper
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ufesa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ultimate
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ultimate Speed
- Niet gecategoriseerd Uni-T
- Niet gecategoriseerd Uniden
- Niet gecategoriseerd Unify
- Niet gecategoriseerd United Office
- Niet gecategoriseerd Universal Remote Control
- Niet gecategoriseerd UPM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Upo
- Niet gecategoriseerd V-Tac
- Niet gecategoriseerd V-Zug
- Niet gecategoriseerd Valeo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Varta
- Niet gecategoriseerd VAX
- Niet gecategoriseerd VCM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Veho
- Niet gecategoriseerd Velbus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Velleman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Velux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Venta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ventura
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ventus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Verbatim
- Niet gecategoriseerd Veritas
- Niet gecategoriseerd Verizon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vermeiren
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vestel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vestfrost
- Niet gecategoriseerd Viatek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vicks
- Niet gecategoriseerd Victor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Viessmann
- Niet gecategoriseerd View Quest
- Niet gecategoriseerd Viewsonic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Viking
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vileda
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vinci
- Niet gecategoriseerd Viper
- Niet gecategoriseerd VirtuFit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vitalmaxx
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vitamix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vitek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vivanco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vivax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vivitar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vivo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vivotek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vizio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vogels
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vogue
- Niet gecategoriseerd Voigtlander
- Niet gecategoriseerd Volkswagen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Voltcraft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vonroc
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vonyx
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vornado
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vortex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wachendorff
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wacom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Waeco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wagner
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wallas
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wamsler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wasco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Waterpik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Watson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Waves
- Niet gecategoriseerd Weasy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Weber
- Niet gecategoriseerd WEG
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wehkamp
- Niet gecategoriseerd Weishaupt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Weller
- Niet gecategoriseerd Welltech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Western Digital
- Niet gecategoriseerd Westfalia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Westinghouse
- Niet gecategoriseerd WHALE
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wharfedale
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wiha
- Niet gecategoriseerd WilTec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Winegard
- Niet gecategoriseerd Winix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Withings
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wmf
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wolf
- Niet gecategoriseerd Woods
- Niet gecategoriseerd Woood
- Niet gecategoriseerd Workzone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Worx
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wurth
- Niet gecategoriseerd X4 Life
- Niet gecategoriseerd X4-Tech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xavax
- Niet gecategoriseerd XGIMI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xlyne
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xoro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xterra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xtorm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xunzel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yaesu
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yale
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ygnis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yongnuo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yphix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yukon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zagg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zalman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zebra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zehnder
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zelmer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zenec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zennio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zepter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ziggo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zipper
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zodiac
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zoofari
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zoom
- Niet gecategoriseerd ZTE
- Niet gecategoriseerd ZyXEL
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jabra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jamo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jane
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jata
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jay-tech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jensen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jilong
- Niet gecategoriseerd JL Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd JML
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jocca
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jocel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Joie
- Niet gecategoriseerd Joovy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jotul
- Niet gecategoriseerd Joy-it
- Niet gecategoriseerd Juki
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jumbo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jung
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jura
- Niet gecategoriseerd Juwel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jysk
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oase
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oceanic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oertli
- Niet gecategoriseerd OJ ELECTRONICS
- Niet gecategoriseerd OK
- Niet gecategoriseerd OKAY
- Niet gecategoriseerd Olimpia Splendid
- Niet gecategoriseerd Olivetti
- Niet gecategoriseerd Olympia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Omega
- Niet gecategoriseerd Omnitronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Omron
- Niet gecategoriseerd One For All
- Niet gecategoriseerd OneConcept
- Niet gecategoriseerd OnePlus
- Niet gecategoriseerd OneTouch
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oppo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Optex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Optoma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Orange
- Niet gecategoriseerd Orbis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Orbit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oregon Scientific
- Niet gecategoriseerd Orion
- Niet gecategoriseerd Osann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Osram
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oster
- Niet gecategoriseerd Otolift
- Niet gecategoriseerd Outdoorchef
- Niet gecategoriseerd Overmax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ozito
- Niet gecategoriseerd SunPower
- Niet gecategoriseerd 3M
- Niet gecategoriseerd Anthem
- Niet gecategoriseerd Christopeit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Clas Ohlson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Concept2
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crivit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cambridge
- Niet gecategoriseerd McIntosh
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vincent
- Niet gecategoriseerd Canicom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Valore
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trimble
- Niet gecategoriseerd Becken
- Niet gecategoriseerd Black And Decker
- Niet gecategoriseerd Camry
- Niet gecategoriseerd Caso
- Niet gecategoriseerd Clatronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Concept
- Niet gecategoriseerd Continental Edison
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crofton
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cuisinart
- Niet gecategoriseerd ECG
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elba
- Niet gecategoriseerd First Austria
- Niet gecategoriseerd Guzzanti
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hamilton Beach
- Niet gecategoriseerd Heinner
- Niet gecategoriseerd Imetec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Izzy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Khind
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mellerware
- Niet gecategoriseerd OBH Nordica
- Niet gecategoriseerd Optimum
- Niet gecategoriseerd Orbegozo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pitsos
- Niet gecategoriseerd Profilo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Scarlett
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sinbo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trisa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wilfa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alpatronix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Audeze
- Niet gecategoriseerd B-Speech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bang And Olufsen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bowers And Wilkins
- Niet gecategoriseerd Caliber
- Niet gecategoriseerd Champion
- Niet gecategoriseerd Connect IT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Creative
- Niet gecategoriseerd CSL
- Niet gecategoriseerd Exibel
- Niet gecategoriseerd GoGEN
- Niet gecategoriseerd JLab
- Niet gecategoriseerd Krüger And Matz
- Niet gecategoriseerd Macally
- Niet gecategoriseerd Monoprice
- Niet gecategoriseerd Naxa
- Niet gecategoriseerd NGS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Niceboy
- Niet gecategoriseerd POGS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Proscan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schwaiger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Shure
- Niet gecategoriseerd Steren
- Niet gecategoriseerd T'nB
- Niet gecategoriseerd Umidigi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Anslut
- Niet gecategoriseerd Barska
- Niet gecategoriseerd Carmen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kayoba
- Niet gecategoriseerd Klein Tools
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lupine
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maglite
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nitecore
- Niet gecategoriseerd Olight
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pelican
- Niet gecategoriseerd Petzl
- Niet gecategoriseerd Princeton Tec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Urrea
- Niet gecategoriseerd Walther
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wetelux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aicon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cocraft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Draper
- Niet gecategoriseerd Meec Tools
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rapid
- Niet gecategoriseerd Senco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Best Fitness
- Niet gecategoriseerd Steelbody
- Niet gecategoriseerd True
- Niet gecategoriseerd Baninni
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lionelo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kunft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Prince
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yamato
- Niet gecategoriseerd Playtive Junior
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zenit
- Niet gecategoriseerd R-Vent
- Niet gecategoriseerd Soler And Palau
- Niet gecategoriseerd Genesis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Leen Bakker
- Niet gecategoriseerd Parisot
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pericles
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tvilum
- Niet gecategoriseerd Svedbergs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vantec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crock-Pot
- Niet gecategoriseerd Instant
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nutrichef
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hilti
- Niet gecategoriseerd Autodesk
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bentley
- Niet gecategoriseerd Corel
- Niet gecategoriseerd DoorBird
- Niet gecategoriseerd Parallels
- Niet gecategoriseerd Safescan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sophos
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ubiquiti Networks
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ferplast
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fluval
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sicce
- Niet gecategoriseerd SuperFish
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tetra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hamron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kraftwerk
- Niet gecategoriseerd Clarion
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sissel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cobra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Deutz
- Niet gecategoriseerd Perkins
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arthur Martin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aspes
- Niet gecategoriseerd AYA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bella
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blanco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bush
- Niet gecategoriseerd Campomatic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Caple
- Niet gecategoriseerd CDA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Comfee
- Niet gecategoriseerd Constructa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Corberó
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crosley
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cylinda
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dacor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Danby
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elektron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Equator
- Niet gecategoriseerd Esatto
- Niet gecategoriseerd Euromaid
- Niet gecategoriseerd Flavel
- Niet gecategoriseerd GAM
- Niet gecategoriseerd EMOS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hobart
- Niet gecategoriseerd Infiniton
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jenn-Air
- Niet gecategoriseerd Televés
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kaiser
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kernau
- Niet gecategoriseerd King
- Niet gecategoriseerd KKT Kolbe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Conceptronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Monogram
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nevir
- Niet gecategoriseerd Orima
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sauter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Simpson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Summit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Svan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aerotec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cotech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Power Craft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tacklife
- Niet gecategoriseerd Truper
- Niet gecategoriseerd DPA
- Niet gecategoriseerd IMG Stageline
- Niet gecategoriseerd MXL
- Niet gecategoriseerd Festo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fieldmann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mafell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tracer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bright Starts
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chicco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Celestron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Levenhuk
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cabasse
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aplic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Metapace
- Niet gecategoriseerd McGregor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stannah
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blackburn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lezyne
- Niet gecategoriseerd Topeak
- Niet gecategoriseerd Babybjörn
- Niet gecategoriseerd BabyDan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Century
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cosatto
- Niet gecategoriseerd Geuther
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ingenuity
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mamas & Papas
- Niet gecategoriseerd Paidi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Silver Cross
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vipack
- Niet gecategoriseerd KidKraft
- Niet gecategoriseerd MADE
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nolte
- Niet gecategoriseerd Samac
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wacker Neuson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Active Era
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ardes
- Niet gecategoriseerd Conair
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cresta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eldom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grunkel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lümme
- Niet gecategoriseerd Miniland
- Niet gecategoriseerd Teesa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Heaven Fresh
- Niet gecategoriseerd Heylo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oreck
- Niet gecategoriseerd Prime3
- Niet gecategoriseerd Proficare
- Niet gecategoriseerd Coline
- Niet gecategoriseerd Haeger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Proctor Silex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Waring Commercial
- Niet gecategoriseerd Black Diamond
- Niet gecategoriseerd Coleman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Easy Camp
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kelty
- Niet gecategoriseerd Outwell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Raclet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rusta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vango
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vaude
- Niet gecategoriseerd Newline
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brondell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Duravit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pressalit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schütte
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arlo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Atlona
- Niet gecategoriseerd Avidsen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hamlet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hive
- Niet gecategoriseerd SereneLife
- Niet gecategoriseerd Davita
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cooler Master
- Niet gecategoriseerd NZXT
- Niet gecategoriseerd SilverStone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thermaltake
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yeyian
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brentwood
- Niet gecategoriseerd Albert Heijn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Proxxon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Marvel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Artusi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cadac
- Niet gecategoriseerd Campart
- Niet gecategoriseerd Char-Broil
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gasmate
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rösle
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kessler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Medel
- Niet gecategoriseerd DCG
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kubo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pyrex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vakoss
- Niet gecategoriseerd Witt
- Niet gecategoriseerd AdHoc
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aarke
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tescoma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arkon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Biltema
- Niet gecategoriseerd Defender
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rocketfish
- Niet gecategoriseerd Topmove
- Niet gecategoriseerd AIC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alba
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elbe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Majestic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Prologue
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trevi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Malmbergs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Porter-Cable
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sun Joe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yard Force
- Niet gecategoriseerd Challenge
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cramer
- Niet gecategoriseerd EGO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gtech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hurricane
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maruyama
- Niet gecategoriseerd Spear & Jackson
- Niet gecategoriseerd BBB
- Niet gecategoriseerd Busch And Müller
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cateye
- Niet gecategoriseerd Goodram
- Niet gecategoriseerd Spanninga
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crunch
- Niet gecategoriseerd ETON
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trasman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cilio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Royal Catering
- Niet gecategoriseerd Calor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gima
- Niet gecategoriseerd LandRoller
- Niet gecategoriseerd Little Giant
- Niet gecategoriseerd Adesso
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rapoo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vivolink
- Niet gecategoriseerd ADATA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crucial
- Niet gecategoriseerd Intel
- Niet gecategoriseerd QOMO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eurolite
- Niet gecategoriseerd BDI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Corsair
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cougar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Interstuhl
- Niet gecategoriseerd Primus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Techly
- Niet gecategoriseerd TOGU
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zuiver
- Niet gecategoriseerd Leatherman
- Niet gecategoriseerd OutNowTech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Contax
- Niet gecategoriseerd GFM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Phase One
- Niet gecategoriseerd Flexispot
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cello
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brydge
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cherry
- Niet gecategoriseerd Deltaco
- Niet gecategoriseerd KeepOut
- Niet gecategoriseerd Natec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ozone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Penclic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Satechi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Savio
- Niet gecategoriseerd SIIG
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sven
- Niet gecategoriseerd Broan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dedra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Graphite
- Niet gecategoriseerd Patriot
- Niet gecategoriseerd RIDGID
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tryton
- Niet gecategoriseerd DSC
- Niet gecategoriseerd GA.MA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Max Pro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Revamp
- Niet gecategoriseerd Visage
- Niet gecategoriseerd Piet Boon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Comelit
- Niet gecategoriseerd M-e
- Niet gecategoriseerd NuTone
- Niet gecategoriseerd REV
- Niet gecategoriseerd CMI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hecht
- Niet gecategoriseerd Herkules
- Niet gecategoriseerd Könner & Söhnen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Avantree
- Niet gecategoriseerd CasaFan
- Niet gecategoriseerd KDK
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kichler
- Niet gecategoriseerd AXI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Quadro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Smoby
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lenoxx
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blow
- Niet gecategoriseerd Scosche
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sensei
- Niet gecategoriseerd Weil
- Niet gecategoriseerd Estella
- Niet gecategoriseerd Riviera And Bar
- Niet gecategoriseerd NUK
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oricom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fisher
- Niet gecategoriseerd 4moms
- Niet gecategoriseerd Anex
- Niet gecategoriseerd BRIO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cybex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Evenflo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Phil And Teds
- Niet gecategoriseerd Genie
- Niet gecategoriseerd ClearOne
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hudora
- Niet gecategoriseerd Forza
- Niet gecategoriseerd Evoc
- Niet gecategoriseerd Osprey
- Niet gecategoriseerd Salewa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bimar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crane
- Niet gecategoriseerd Goodway
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lasko
- Niet gecategoriseerd The Grainfather
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cata
- Niet gecategoriseerd U-Line
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zephyr
- Niet gecategoriseerd 4smarts
- Niet gecategoriseerd Duracell
- Niet gecategoriseerd C3
- Niet gecategoriseerd MiPow
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cosori
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tripp Lite
- Niet gecategoriseerd Veripart
- Niet gecategoriseerd Baby Brezza
- Niet gecategoriseerd Creda
- Niet gecategoriseerd James
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chacon
- Niet gecategoriseerd MSW
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ordex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Safco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Carpigiani
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hard Head
- Niet gecategoriseerd Unilux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Naish
- Niet gecategoriseerd Woonexpress
- Niet gecategoriseerd Caberg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lazer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schuberth
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dr. Browns
- Niet gecategoriseerd TRIUS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lantus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Novo Nordisk
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sanofi
- Niet gecategoriseerd American DJ
- Niet gecategoriseerd Antari
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chauvet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Exagerate
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mr. Heater
- Niet gecategoriseerd SHX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tesy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Foster
- Niet gecategoriseerd ACE
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nexa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Swann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Woox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Musical Fidelity
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nûby
- Niet gecategoriseerd Baby Trend
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lindam
- Niet gecategoriseerd Valcom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Capital Sports
- Niet gecategoriseerd Carnielli
- Niet gecategoriseerd Integra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Peloton
- Niet gecategoriseerd Craftsman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rikon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vroomshoop
- Niet gecategoriseerd Honey-Can-Do
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kwantum
- Niet gecategoriseerd Camec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Godrej
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tiny Love
- Niet gecategoriseerd Milectric
- Niet gecategoriseerd Morris
- Niet gecategoriseerd Orava
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rommer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Signature
- Niet gecategoriseerd Simplicity
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dash
- Niet gecategoriseerd ASSA ABLOY
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dorma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dormakaba
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eurospec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nilox
- Niet gecategoriseerd CaterChef
- Niet gecategoriseerd Approx
- Niet gecategoriseerd Billow
- Niet gecategoriseerd SPC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sungale
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cecotec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Baxi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beretta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Milan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Q-CONNECT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Best
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nodor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thermex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Canyon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cisco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Foreo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oromed
- Niet gecategoriseerd SureFlap
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schumacher
- Niet gecategoriseerd ARRI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Verto
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sanus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hamax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alphacool
- Niet gecategoriseerd AZZA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Enermax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Noctua
- Niet gecategoriseerd SainSmart
- Niet gecategoriseerd Seville Classics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bauhn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Block
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pro-Ject
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rega
- Niet gecategoriseerd Moldex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ledger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Contour
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cowon
- Niet gecategoriseerd EVOLVEO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Prixton
- Niet gecategoriseerd Whistler
- Niet gecategoriseerd JOBY
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vello
- Niet gecategoriseerd Snow Joe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cruz
- Niet gecategoriseerd G3
- Niet gecategoriseerd Flama
- Niet gecategoriseerd Weston
- Niet gecategoriseerd Victron Energy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Carrier
- Niet gecategoriseerd Delta Dore
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fantini Cosmi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vemer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Warmup
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nesco
- Niet gecategoriseerd RGV
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vision
- Niet gecategoriseerd LC-Power
- Niet gecategoriseerd ZOTAC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Matrox
- Niet gecategoriseerd MBM
- Niet gecategoriseerd True & Tidy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vanish
- Niet gecategoriseerd Goldtouch
- Niet gecategoriseerd HyperX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Compex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Atomos
- Niet gecategoriseerd Natuzzi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Polisport
- Niet gecategoriseerd AMC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Citronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crown
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dynacord
- Niet gecategoriseerd Phonic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yorkville
- Niet gecategoriseerd De Buyer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Catit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lund
- Niet gecategoriseerd Apelson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Benavent
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eico
- Niet gecategoriseerd Furrion
- Niet gecategoriseerd Coby
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rinnai
- Niet gecategoriseerd MedFolio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Asustor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Infasecure
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sparco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gefen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Deltronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ei Electronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fibaro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fito
- Niet gecategoriseerd GEV
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kidde
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crosscall
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maze
- Niet gecategoriseerd Minn Kota
- Niet gecategoriseerd Plum
- Niet gecategoriseerd DMax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jupiter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Peach
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rexel
- Niet gecategoriseerd CradlePoint
- Niet gecategoriseerd Juniper
- Niet gecategoriseerd Planet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Innr
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lucide
- Niet gecategoriseerd Massive
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maul
- Niet gecategoriseerd Paulmann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bixolon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brady
- Niet gecategoriseerd Datacard
- Niet gecategoriseerd GoDEX
- Niet gecategoriseerd WEN
- Niet gecategoriseerd Genelec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cardiostrong
- Niet gecategoriseerd Barkan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bretford
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chief
- Niet gecategoriseerd Doffler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gabor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Marker
- Niet gecategoriseerd Debel
- Niet gecategoriseerd AcuRite
- Niet gecategoriseerd Etekcity
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dahle
- Niet gecategoriseerd Audix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Califone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Swingline
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chamberlain
- Niet gecategoriseerd Munchkin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lescha
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tornado
- Niet gecategoriseerd Imperia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Steiner
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zeiss
- Niet gecategoriseerd Buzz Rack
- Niet gecategoriseerd Masterbuilt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Testo
- Niet gecategoriseerd WAGAN
- Niet gecategoriseerd Viridian
- Niet gecategoriseerd Respironics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cressi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Burigotto
- Niet gecategoriseerd System Sensor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Exit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Springfree
- Niet gecategoriseerd Intellinet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Avocor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eastron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Energenie
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cubot
- Niet gecategoriseerd NUX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thomann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Karma
- Niet gecategoriseerd HeartSine
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sunding
- Niet gecategoriseerd DoubleSight
- Niet gecategoriseerd Accucold
- Niet gecategoriseerd Acros
- Niet gecategoriseerd Husky
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lec
- Niet gecategoriseerd BabyOno
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lansinoh
- Niet gecategoriseerd Neno
- Niet gecategoriseerd Carson
- Niet gecategoriseerd FIMI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Monster
- Niet gecategoriseerd Artrom
- Niet gecategoriseerd ISi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bron-Coucke
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dreambaby
- Niet gecategoriseerd Swift
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ansco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cosina
- Niet gecategoriseerd Graflex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ilford
- Niet gecategoriseerd Petri
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cleanmaxx
- Niet gecategoriseerd BCA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mammut
- Niet gecategoriseerd FIAP
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pontec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xblitz
- Niet gecategoriseerd West Elm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hoshizaki
- Niet gecategoriseerd Clearblue
- Niet gecategoriseerd CyberPower
- Niet gecategoriseerd Coolaroo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Razor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Babylonia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Infantino
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kolcraft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Manduca
- Niet gecategoriseerd Havis
- Niet gecategoriseerd I-Tec
- Niet gecategoriseerd SEIKI
- Niet gecategoriseerd SunBriteTV
- Niet gecategoriseerd Magnus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Manfrotto
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sachtler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sevenoak
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zhiyun
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beautifly
- Niet gecategoriseerd Holman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stabila
- Niet gecategoriseerd Testboy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alpha Tools
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hazet
- Niet gecategoriseerd 3B
- Niet gecategoriseerd ResMed
- Niet gecategoriseerd Supermicro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bobrick
- Niet gecategoriseerd Newport Brass
- Niet gecategoriseerd Purell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Harley Benton
- Niet gecategoriseerd Clage
- Niet gecategoriseerd Damixa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elkay
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gustavsberg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oras
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sloan
- Niet gecategoriseerd TOTO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sime
- Niet gecategoriseerd G-Technology
- Niet gecategoriseerd Platinum
- Niet gecategoriseerd CGV
- Niet gecategoriseerd Heitech
- Niet gecategoriseerd LTC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Full Boar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yato
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cabstone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cardo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dreamgear
- Niet gecategoriseerd Interphone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jonsered
- Niet gecategoriseerd Qualcast
- Niet gecategoriseerd Total
- Niet gecategoriseerd Singercon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dynamic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Karibu
- Niet gecategoriseerd Reber
- Niet gecategoriseerd SKROSS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aida
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ninebot
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cottons
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bestgreen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gianni Ferrari
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hayter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Masport
- Niet gecategoriseerd Morrison
- Niet gecategoriseerd Livall
- Niet gecategoriseerd Proteca
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tripp
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ankarsrum
- Niet gecategoriseerd Galcon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nelson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Barazza
- Niet gecategoriseerd Winia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bravilor
- Niet gecategoriseerd ZAZU
- Niet gecategoriseerd Growatt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lenmar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Exo-Terra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lexar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lindy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nordea
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xcellon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Euro Cuisine
- Niet gecategoriseerd OSO
- Niet gecategoriseerd AVerMedia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lumens
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jabsco
- Niet gecategoriseerd TensCare
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ovente
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ursus Trotter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nanni
- Niet gecategoriseerd Herlag
- Niet gecategoriseerd Roba
- Niet gecategoriseerd MOZA
- Niet gecategoriseerd IOGEAR
- Niet gecategoriseerd Séura
- Niet gecategoriseerd Basbau
- Niet gecategoriseerd ELO
- Niet gecategoriseerd SVAT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stalco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Petmate
- Niet gecategoriseerd Black Box
- Niet gecategoriseerd Auto Joe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fortinet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Youin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Croozer
- Niet gecategoriseerd IFM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Perfecta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cricut
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hähnel
- Niet gecategoriseerd DataVideo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Be Quiet!
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kindermann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Berg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Simplified MFG
- Niet gecategoriseerd GLP
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hombli
- Niet gecategoriseerd Powertec
- Niet gecategoriseerd ART
- Niet gecategoriseerd Valeton
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tiptop Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Summit Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd SKS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Musway
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wago
- Niet gecategoriseerd Smith & Wesson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Avalon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Plant Craft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dubatti
- Niet gecategoriseerd Baumr-AG
- Niet gecategoriseerd GW Instek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Totolink
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vaddio
- Niet gecategoriseerd La Crosse Technology
- Niet gecategoriseerd HK Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bogen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Da-Lite
- Niet gecategoriseerd CaterCool
- Niet gecategoriseerd Allen & Heath
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ariston Thermo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kyoritsu
- Niet gecategoriseerd Air King
- Niet gecategoriseerd SBS
- Niet gecategoriseerd KiddyGuard
- Niet gecategoriseerd AJA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Galaxy Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Adj
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ikan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dahua Technology
- Niet gecategoriseerd AV:link
- Niet gecategoriseerd Neumann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Native Instruments
- Niet gecategoriseerd Walkstool
- Niet gecategoriseerd Apogee
- Niet gecategoriseerd Peerless-AV
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pyle Pro
- Niet gecategoriseerd PreSonus
- Niet gecategoriseerd NOCO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Inkbird
- Niet gecategoriseerd Electro-Voice
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mercusys
- Niet gecategoriseerd Playseat
- Niet gecategoriseerd Weihrauch Sport
- Niet gecategoriseerd Martha Stewart
- Niet gecategoriseerd Reolink
- Niet gecategoriseerd Glem Gas
- Niet gecategoriseerd IK Multimedia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elation
- Niet gecategoriseerd IDance
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rupert Neve Designs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Carel
- Niet gecategoriseerd BOHLT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Simplecom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Speed-Link
- Niet gecategoriseerd Endress
- Niet gecategoriseerd Millenium
- Niet gecategoriseerd Owon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aqua Joe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Valueline
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chandler
- Niet gecategoriseerd RDL
- Niet gecategoriseerd Austrian Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Busch-Jaeger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cellular Line
- Niet gecategoriseerd EVE
- Niet gecategoriseerd Countryman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chord
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fredenstein
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aruba
- Niet gecategoriseerd Swissonic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sound Machines
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aviom
- Niet gecategoriseerd QSC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Happy Plugs
- Niet gecategoriseerd BABY Born
- Niet gecategoriseerd Levoit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Traxxas
- Niet gecategoriseerd Audac
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eltako
- Niet gecategoriseerd Azden
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aerial
- Niet gecategoriseerd ESI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grillmeister
- Niet gecategoriseerd For_Q
- Niet gecategoriseerd GVM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Coyote
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rain Bird
- Niet gecategoriseerd Irritrol
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kasda
- Niet gecategoriseerd Marshall Electronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Shuttle
- Niet gecategoriseerd Puky
- Niet gecategoriseerd GFI System
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ctek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Swarovski Optik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vacmaster
- Niet gecategoriseerd Golden Age Project
- Niet gecategoriseerd Spin Master
- Niet gecategoriseerd Huion
- Niet gecategoriseerd TC Electronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd BOYA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rode
- Niet gecategoriseerd 4ms
- Niet gecategoriseerd Anchor Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dantherm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Projecta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lyman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Genaray
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cablexpert
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stelton
- Niet gecategoriseerd DAS Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eventide
- Niet gecategoriseerd Radial Engineering
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blackmagic Design
- Niet gecategoriseerd Noveen
- Niet gecategoriseerd ATen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cre8audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nanlite
- Niet gecategoriseerd BakkerElkhuizen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Boyo
- Niet gecategoriseerd IKRA
- Niet gecategoriseerd IOttie
- Niet gecategoriseerd Profoto
- Niet gecategoriseerd XPG
- Niet gecategoriseerd Namco Bandai Games
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trio Lighting
- Niet gecategoriseerd Valco Baby
- Niet gecategoriseerd Argoclima
- Niet gecategoriseerd Metra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hestan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cadel
- Niet gecategoriseerd ThinkFun
- Niet gecategoriseerd Miggo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Russound
- Niet gecategoriseerd ISDT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Abac
- Niet gecategoriseerd Slik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Celly
- Niet gecategoriseerd Skan Holz
- Niet gecategoriseerd Comica
- Niet gecategoriseerd CRUX
- Niet gecategoriseerd ZLine
- Niet gecategoriseerd Audient
- Niet gecategoriseerd Heller
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hegel
- Niet gecategoriseerd RGBlink
- Niet gecategoriseerd EMSA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Waldbeck
- Niet gecategoriseerd CTA Digital
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bazooka
- Niet gecategoriseerd PAX
- Niet gecategoriseerd K&K Sound
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dutchbone
- Niet gecategoriseerd MyPhone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fanvil
- Niet gecategoriseerd Noise Engineering
- Niet gecategoriseerd PAC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wentronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xtreme
- Niet gecategoriseerd RAVPower
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mooer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hooker
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dynaudio
- Niet gecategoriseerd August
- Niet gecategoriseerd Adder
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gitzo
- Niet gecategoriseerd DBX
- Niet gecategoriseerd ECS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Selec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aiphone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tivoli Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Senal
- Niet gecategoriseerd JETI
- Niet gecategoriseerd EQ3
- Niet gecategoriseerd Karlik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Comark
- Niet gecategoriseerd Homematic IP
- Niet gecategoriseerd N8WERK
- Niet gecategoriseerd Calex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Clean Air Optima
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tovsto
- Niet gecategoriseerd Learning Resources
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xaoc
- Niet gecategoriseerd Qute
- Niet gecategoriseerd Victrola
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lanberg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kopul
- Niet gecategoriseerd AENO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Proaim
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nexxt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Glock
- Niet gecategoriseerd Linn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Martin Logan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vorago
- Niet gecategoriseerd Anton/Bauer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Extron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ibiza Sound
- Niet gecategoriseerd Promethean
- Niet gecategoriseerd HyperIce
- Niet gecategoriseerd Basil
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chipolino
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nxg
- Niet gecategoriseerd AGM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ambient Recording
- Niet gecategoriseerd Diana
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tandberg Data
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fostex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Prowise
- Niet gecategoriseerd Impact
- Niet gecategoriseerd Areca
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mousetrapper
- Niet gecategoriseerd TSC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sikkens
- Niet gecategoriseerd DEXP
- Niet gecategoriseerd Burris
- Niet gecategoriseerd GolfBuddy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Proel
- Niet gecategoriseerd FBT
- Niet gecategoriseerd NodOn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Edge
- Niet gecategoriseerd Endorphin.es
- Niet gecategoriseerd MIPRO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bracketron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Solid State Logic
- Niet gecategoriseerd XYZprinting
- Niet gecategoriseerd Computherm
- Niet gecategoriseerd MTM
- Niet gecategoriseerd X-Sense
- Niet gecategoriseerd IMC Toys
- Niet gecategoriseerd Neets
- Niet gecategoriseerd NAV-TV
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wooden Camera
- Niet gecategoriseerd AMX
- Niet gecategoriseerd SEH
- Niet gecategoriseerd AudioQuest
- Niet gecategoriseerd Powerblade
- Niet gecategoriseerd HiFi ROSE
- Niet gecategoriseerd OSD Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd WMD
- Niet gecategoriseerd Andover
- Niet gecategoriseerd Moog
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arctic Cooling
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blackstar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ergotron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Equip
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stairville
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crestron
- Niet gecategoriseerd RME
- Niet gecategoriseerd Black Lion Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crayola
- Niet gecategoriseerd Avid
- Niet gecategoriseerd CTOUCH
- Niet gecategoriseerd Adastra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Konig & Meyer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Meister Craft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yeastar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Laserworld
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chuango
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hori
- Niet gecategoriseerd Klavis
- Niet gecategoriseerd ORNO
- Niet gecategoriseerd ETiger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bison
- Niet gecategoriseerd Foxconn
- Niet gecategoriseerd EMG
- Niet gecategoriseerd Icy Dock
- Niet gecategoriseerd Make Noise
- Niet gecategoriseerd TeachLogic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maytronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Charge Amps
- Niet gecategoriseerd Newland
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aeon Labs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Shokz
- Niet gecategoriseerd TEF
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dreame
- Niet gecategoriseerd Life Gear
- Niet gecategoriseerd SMART Technologies
- Niet gecategoriseerd ZYCOO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kontakt Chemie
- Niet gecategoriseerd Riccar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Clean Paper
- Niet gecategoriseerd OpenVox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Electro Harmonix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Erica Synths
- Niet gecategoriseerd SkyRC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Atdec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Portech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Markbass
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kugoo
- Niet gecategoriseerd StarTech.com
- Niet gecategoriseerd Style Me Up
- Niet gecategoriseerd Flexson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rossi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nimble
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eissound
- Niet gecategoriseerd Everdure
- Niet gecategoriseerd TCM FX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Snakebyte
- Niet gecategoriseerd IBasso
- Niet gecategoriseerd Warm Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd AudioControl
- Niet gecategoriseerd Purpleline
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nerf
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nature's Truth
- Niet gecategoriseerd Emeril Lagasse
- Niet gecategoriseerd 2hp
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kelkay
- Niet gecategoriseerd Baby Annabell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crane Song
- Niet gecategoriseerd PureLink
- Niet gecategoriseerd HyperJuice
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ruger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sonnet
- Niet gecategoriseerd UX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gamdias
- Niet gecategoriseerd SPL
- Niet gecategoriseerd Multimetrix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Solid
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hubelino
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aputure
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gerni
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jupio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Infomir
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blaser
- Niet gecategoriseerd Heatit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Deaf Bonce
- Niet gecategoriseerd ProForm
- Niet gecategoriseerd UTEPO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lindell Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Think Tank
- Niet gecategoriseerd Timbersled
- Niet gecategoriseerd After Later Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Twelve South
- Niet gecategoriseerd Koala
- Niet gecategoriseerd Drawmer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blue Sky
- Niet gecategoriseerd ColorKey
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thronmax
- Niet gecategoriseerd PowerXL
- Niet gecategoriseerd IXS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Etymotic
- Niet gecategoriseerd AirTurn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Turbo Air
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zega
- Niet gecategoriseerd Morningstar
- Niet gecategoriseerd CreativeWorKs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beghelli
- Niet gecategoriseerd Advantech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Moxa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ultimate Support
- Niet gecategoriseerd Smart-AVI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Inter-Tech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mesa Boogie
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bicker Elektronik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Iadea
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blizzard
- Niet gecategoriseerd Biohort
- Niet gecategoriseerd Reginox
- Niet gecategoriseerd BIOS Medical
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eero
- Niet gecategoriseerd PSSO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wise
- Niet gecategoriseerd SIG Sauer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Merkel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Patching Panda
- Niet gecategoriseerd AudioThing
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cinderella
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crest Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Globe
- Niet gecategoriseerd XS Power
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beautiful
- Niet gecategoriseerd Anthro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Martin Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grace Design
- Niet gecategoriseerd Contour Design
- Niet gecategoriseerd Heckler Design
- Niet gecategoriseerd Propellerhead
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nanuk
- Niet gecategoriseerd Digital Watchdog
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sonifex
- Niet gecategoriseerd EcoFlow
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kreiling
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xantech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Scanstrut
- Niet gecategoriseerd Roadinger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Boori
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oklahoma Sound
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brilliant
- Niet gecategoriseerd Philos
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thames & Kosmos
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kali Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Audioengine
- Niet gecategoriseerd Betso
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fortia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Moen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kramer
- Niet gecategoriseerd IFi Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Babysense
- Niet gecategoriseerd VS Sassoon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Revel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sealy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wet Sounds
- Niet gecategoriseerd CRU
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mean Well
- Niet gecategoriseerd Avantone Pro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sanitaire
- Niet gecategoriseerd Umarex
- Niet gecategoriseerd AbleNet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Exalux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bolt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Leap Frog
- Niet gecategoriseerd Calligaris .com
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sightmark
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hughes & Kettner
- Niet gecategoriseerd Manley
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rothenberger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Micro Matic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Motu
- Niet gecategoriseerd Creamsource
- Niet gecategoriseerd MEE Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thermomate
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kingston
- Niet gecategoriseerd Noris
- Niet gecategoriseerd Acard
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gamewright
- Niet gecategoriseerd Guide
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hameg
- Niet gecategoriseerd HammerSmith
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jordan
- Niet gecategoriseerd King Craft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Panta
- Niet gecategoriseerd Physa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Roidmi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sonel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ugreen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ulsonix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Uniprodo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vixen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xplora
- Niet gecategoriseerd Norton Clipper
- Niet gecategoriseerd KanexPro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blustream
- Niet gecategoriseerd Avocent
- Niet gecategoriseerd SVS
- Niet gecategoriseerd YSI
- Niet gecategoriseerd RTS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ontech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Koss
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kwikset
- Niet gecategoriseerd RaySafe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Di4
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ashly
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sanli
- Niet gecategoriseerd Shelly
- Niet gecategoriseerd Siemon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Block & Block
- Niet gecategoriseerd Four Hands
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oben
- Niet gecategoriseerd ASA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Botex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maxsa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Park Tool
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dangerous Music
- Niet gecategoriseerd ModeCom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fine Dine
- Niet gecategoriseerd Essenza
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rugged Geek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dave Smith
- Niet gecategoriseerd PATLITE
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lian Li
- Niet gecategoriseerd Match
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vocopro
- Niet gecategoriseerd TFA Dostmann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Werma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Walrus Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Durable
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zenza Bronica
- Niet gecategoriseerd Greisinger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Suprema
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ziehl
- Niet gecategoriseerd VAIS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Glide Gear
- Niet gecategoriseerd Perma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Scandes
- Niet gecategoriseerd Testec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Enovate
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pigtronix
- Niet gecategoriseerd ProTeam
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wagner SprayTech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Libec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pardini
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ledlenser
- Niet gecategoriseerd KWC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Soul
- Niet gecategoriseerd Laney
- Niet gecategoriseerd BirdDog
- Niet gecategoriseerd Theragun
- Niet gecategoriseerd LAS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rosseto
- Niet gecategoriseerd Redrock Micro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kata
- Niet gecategoriseerd AVer
- Niet gecategoriseerd EarthQuaker Devices
- Niet gecategoriseerd Briggs & Stratton
- Niet gecategoriseerd USAopoly
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gami
- Niet gecategoriseerd Igloohome
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elinchrom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Universal Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd CamRanger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Madrix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Spacedec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Auray
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bontempi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Summer Infant
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cooper & Quint
- Niet gecategoriseerd Deltex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Adax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crimson
- Niet gecategoriseerd OXO Good Grips
- Niet gecategoriseerd Helios Preisser
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nitek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Snoes
- Niet gecategoriseerd Posiflex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Labelmate
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schertler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Teradek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kunath
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hikmicro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vimar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Escort
- Niet gecategoriseerd SolarEdge
- Niet gecategoriseerd GOgroove
- Niet gecategoriseerd ViewCast
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wolfcraft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tennsco
- Niet gecategoriseerd RAM Mounts
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ocean Matrix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Novus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Getac
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arebos
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kreg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Speco Technologies
- Niet gecategoriseerd Backyard Discovery
- Niet gecategoriseerd Minuteman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ortofon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cameo
- Niet gecategoriseerd RéVive
- Niet gecategoriseerd NovaStar
- Niet gecategoriseerd ZKTeco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Merax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Star Micronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kemo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Woodland Scenics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chapin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Morel
- Niet gecategoriseerd J. Rockett Audio Designs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pancontrol
- Niet gecategoriseerd SRS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Satisfyer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hämmerli
- Niet gecategoriseerd Soma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Koliber
- Niet gecategoriseerd Point 65
- Niet gecategoriseerd ReTrak
- Niet gecategoriseerd Akuvox
- Niet gecategoriseerd LYYT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Old Blood Noise
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vulcan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rovo Kids
- Niet gecategoriseerd Catalyst
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dension
- Niet gecategoriseerd Antelope Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Venom
- Niet gecategoriseerd H-Tronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd CE Labs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Legrand
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ebro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Z CAM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Digium
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bluetti
- Niet gecategoriseerd Panduit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Socomec
- Niet gecategoriseerd San Jamar
- Niet gecategoriseerd IPort
- Niet gecategoriseerd X-Rite
- Niet gecategoriseerd Talkaphone
- Niet gecategoriseerd GermGuardian
- Niet gecategoriseerd R-Go Tools
- Niet gecategoriseerd Urbanista
- Niet gecategoriseerd SLV
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sagitter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gagato
- Niet gecategoriseerd Traeger
- Niet gecategoriseerd General
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ooni
- Niet gecategoriseerd Special-T
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tzumi
- Niet gecategoriseerd BERTSCHAT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Michael Todd Beauty
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cygnett
- Niet gecategoriseerd Victorio
- Niet gecategoriseerd JAYS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Intertechno
- Niet gecategoriseerd Parklands
- Niet gecategoriseerd Consul
- Niet gecategoriseerd EKO
- Niet gecategoriseerd BIG
- Niet gecategoriseerd SureFire
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kenton
- Niet gecategoriseerd DAB
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cypress
- Niet gecategoriseerd Foliatec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Röhm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mauser
- Niet gecategoriseerd Silhouette
- Niet gecategoriseerd South Shore
- Niet gecategoriseerd Discovery
- Niet gecategoriseerd T4E
- Niet gecategoriseerd Speck
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tineco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Generation
- Niet gecategoriseerd 8BitDo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dawn House
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ecler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Turbosound
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ulanzi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Anova
- Niet gecategoriseerd Viscount
- Niet gecategoriseerd JennAir
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pawa
- Niet gecategoriseerd LERAN
- Niet gecategoriseerd Majella
- Niet gecategoriseerd GMB Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ashdown Engineering
- Niet gecategoriseerd Unger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Esotec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Petkit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Peltor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pit Boss
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fuzzix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kitchen Brains
- Niet gecategoriseerd Challenge Xtreme
- Niet gecategoriseerd Flycam
- Niet gecategoriseerd NetAlly
- Niet gecategoriseerd JAR Systems
- Niet gecategoriseerd Moleskine
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bytecc
- Niet gecategoriseerd Strex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Premier Mounts
- Niet gecategoriseerd One Stop Systems
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cool Maker
- Niet gecategoriseerd PeakTech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Neo
- Niet gecategoriseerd EVOline
- Niet gecategoriseerd T.I.P.
- Niet gecategoriseerd DoughXpress
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gravity
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aquatic AV
- Niet gecategoriseerd Parasound
- Niet gecategoriseerd MSR
- Niet gecategoriseerd DB Technologies
- Niet gecategoriseerd Promate
- Niet gecategoriseerd Berger & Schröter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tru Components
- Niet gecategoriseerd Step2
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crystal Quest
- Niet gecategoriseerd Emko
- Niet gecategoriseerd Needit
- Niet gecategoriseerd GoldenEar Technology
- Niet gecategoriseerd Colt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elite Screens
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sungrow
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ultron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Choice
- Niet gecategoriseerd Roswell
- Niet gecategoriseerd FOX ESS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Airman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cascade Audio Engineering
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grosfillex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Solplanet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beemoo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hollyland
- Niet gecategoriseerd Versare
- Niet gecategoriseerd Enphase
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tractive
- Niet gecategoriseerd SpeakerCraft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Celexon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Epcom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kanto
- Niet gecategoriseerd ZeeVee
- Niet gecategoriseerd Siku
- Niet gecategoriseerd ADDAC System
- Niet gecategoriseerd Doomoo
- Niet gecategoriseerd MBZ
- Niet gecategoriseerd Davey
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mettler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Metalux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Potenza
- Niet gecategoriseerd LOQED
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hatco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bugera
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fulgor Milano
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mitsai
- Niet gecategoriseerd Leef
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hovicon
- Niet gecategoriseerd RCBS
- Niet gecategoriseerd American BioTech Supply
- Niet gecategoriseerd JANDY
- Niet gecategoriseerd KS Tools
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schmidt & Bender
- Niet gecategoriseerd Improv
- Niet gecategoriseerd InLine
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wegman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lockncharge
- Niet gecategoriseerd V7
- Niet gecategoriseerd Goal Zero
- Niet gecategoriseerd HealthPostures
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dreadbox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Joranalogue
- Niet gecategoriseerd CYP
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lutec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Champion Sports
- Niet gecategoriseerd Molotow
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Miditech
- Niet gecategoriseerd SE Electronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd TTM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Paw Patrol
- Niet gecategoriseerd LELO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Apricorn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Creality3D
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mermade
- Niet gecategoriseerd MXR
- Niet gecategoriseerd SKLZ
- Niet gecategoriseerd Herma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cyrus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Syrp
- Niet gecategoriseerd Losi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ugolini
- Niet gecategoriseerd Heckler & Koch
- Niet gecategoriseerd Palmer
- Niet gecategoriseerd J5create
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hushmat
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tema
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xigmatek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Intellijel
- Niet gecategoriseerd ALM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Topaz
- Niet gecategoriseerd Toddy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Astell&Kern
- Niet gecategoriseerd Doepfer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fun Generation
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xvive
- Niet gecategoriseerd TV One
- Niet gecategoriseerd Empress Effects
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elcom
- Niet gecategoriseerd DataComm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Powercube
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kasp
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dimavery
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hanwha
- Niet gecategoriseerd WestBend
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sherlock
- Niet gecategoriseerd SEA-PRO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Livarno Lux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Omiindustriies
- Niet gecategoriseerd Weltevree
- Niet gecategoriseerd Phoenix Contact
- Niet gecategoriseerd AMS Neve
- Niet gecategoriseerd LVSUN
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aston Microphones
- Niet gecategoriseerd Netsys
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alfi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Polarlite
- Niet gecategoriseerd Companion
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mr. Beams
- Niet gecategoriseerd Morphor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lapp
- Niet gecategoriseerd XO
- Niet gecategoriseerd PcDuino
- Niet gecategoriseerd LECO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maretron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hortus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Razorri
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fetch
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zoetis
- Niet gecategoriseerd NWS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Scale Computing
- Niet gecategoriseerd Broil King
- Niet gecategoriseerd Naturn Living
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aeotec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Catlink
- Niet gecategoriseerd FitterFirst
- Niet gecategoriseerd Raveland
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trumeter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Seidio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sincreative
- Niet gecategoriseerd JDC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hidrate
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sonicware
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nexibo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jolin
- Niet gecategoriseerd MoTip
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stenda
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pro-Lift
- Niet gecategoriseerd HIOAZO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Malstrom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Laserluchs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Powersoft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Casetastic
- Niet gecategoriseerd UClear
- Niet gecategoriseerd BikeLogger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tor Rey
- Niet gecategoriseerd Momo Design
- Niet gecategoriseerd Flavour Blaster
- Niet gecategoriseerd Esdec
- Niet gecategoriseerd TDK-Lambda
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ruark Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd AJH Synth
- Niet gecategoriseerd LifeStraw
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lincoln Electric
- Niet gecategoriseerd Toolit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Egnater
- Niet gecategoriseerd DutchOne
- Niet gecategoriseerd Feitian
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cranborne Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ergie
- Niet gecategoriseerd Reltech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Armcross
- Niet gecategoriseerd Focus Electrics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Huntleigh
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beeletix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gehmann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Batronix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Franzis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gridbyt
- Niet gecategoriseerd LONQ
- Niet gecategoriseerd Em-Trak
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wonky Monkey
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dresden Elektronik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Atmel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Esoteric
- Niet gecategoriseerd SmartAVI
- Niet gecategoriseerd EPH Elektronik
- Niet gecategoriseerd InfiRay
- Niet gecategoriseerd Best Service
- Niet gecategoriseerd IMG Stage Line
- Niet gecategoriseerd IMAC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Metz Connect
- Niet gecategoriseerd MGL Avionics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eikon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Casablanca
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nemco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wireless Solution
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beverage-Air
- Niet gecategoriseerd Barber Tech
- Niet gecategoriseerd EarFun
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oehlbach
- Niet gecategoriseerd Minkels
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kipor
- Niet gecategoriseerd HMS Premium
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arduino
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ave Six
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bestar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pelco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gardigo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Highpoint
- Niet gecategoriseerd Netter Vibration
- Niet gecategoriseerd Puls Dimension
- Niet gecategoriseerd Studiologic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fischer Amps
- Niet gecategoriseerd CHINT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rigol
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sirus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Leviton
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chauvin Arnoux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gretsch
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pentacon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Atlas Sound
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bolsey
- Niet gecategoriseerd Louis Tellier
- Niet gecategoriseerd EtiamPro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Baracuda
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kstar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Neutrik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aim TTi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Air Guard
- Niet gecategoriseerd MediaMatrix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Anywhere Cart
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tuur
- Niet gecategoriseerd ONE Smart Control
- Niet gecategoriseerd Edelkrone
- Niet gecategoriseerd OBSBOT
- Niet gecategoriseerd DEHN
- Niet gecategoriseerd InSinkErator
- Niet gecategoriseerd AREXX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Omnires
- Niet gecategoriseerd Piko
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elite Force
- Niet gecategoriseerd JK Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lifan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jomox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pentatech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lexicon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Icarus Blue
- Niet gecategoriseerd Command
- Niet gecategoriseerd Starburst
- Niet gecategoriseerd Futurelight
- Niet gecategoriseerd AVPro Edge
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fluance
- Niet gecategoriseerd Garden Place
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cudy
- Niet gecategoriseerd MaximaVida
- Niet gecategoriseerd KRK
- Niet gecategoriseerd Robinhood
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bliss Outdoors
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fontiso
- Niet gecategoriseerd Varytec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Altra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Omnilux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Belena
- Niet gecategoriseerd Socket Mobile
- Niet gecategoriseerd Quartet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Heitronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Shadow
- Niet gecategoriseerd IP-COM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kiev
- Niet gecategoriseerd Comtek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fishman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tams Elektronik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Digital Juice
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eschenbach
- Niet gecategoriseerd Neumärker
- Niet gecategoriseerd ASM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ltech
- Niet gecategoriseerd RetroSound
- Niet gecategoriseerd PowerBass
- Niet gecategoriseerd Caroline
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zomo
- Niet gecategoriseerd VAIS Technology
- Niet gecategoriseerd NEO Tools
- Niet gecategoriseerd Synco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Buchla & TipTop Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kiloview
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pyramid
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maico
- Niet gecategoriseerd On-Q
- Niet gecategoriseerd Govee
- Niet gecategoriseerd SetonixSynth
- Niet gecategoriseerd Horex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Inno-Hit
- Niet gecategoriseerd AvaValley
- Niet gecategoriseerd INTIMINA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Monzana
- Niet gecategoriseerd FCC BBQ
- Niet gecategoriseerd Auto XS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Toomax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aqua Marina
- Niet gecategoriseerd Greemotion
- Niet gecategoriseerd Winter Modular
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jonard Tools
- Niet gecategoriseerd FED
- Niet gecategoriseerd Platinum Tools
- Niet gecategoriseerd Synamodec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grotime
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pico Macom
- Niet gecategoriseerd RadonTec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Katrin
- Niet gecategoriseerd TDE Instruments
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kendau
- Niet gecategoriseerd Coxreels
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nous
- Niet gecategoriseerd Morley
- Niet gecategoriseerd Overade
- Niet gecategoriseerd Liemke
- Niet gecategoriseerd Copco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vanson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Carcomm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Swedish Posture
- Niet gecategoriseerd GoldAir
- Niet gecategoriseerd JIMMY
- Niet gecategoriseerd Melnor
- Niet gecategoriseerd CDVI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sôlt
- Niet gecategoriseerd HomePilot
- Niet gecategoriseerd Leaptel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lifenaxx
- Niet gecategoriseerd Waterbird
- Niet gecategoriseerd WindFall
- Niet gecategoriseerd Angler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Akrobat
- Niet gecategoriseerd Casaria
- Niet gecategoriseerd Selleys
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ameristep
- Niet gecategoriseerd KM-fit
- Niet gecategoriseerd X Rocker
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mircom
- Niet gecategoriseerd ESUN
- Niet gecategoriseerd Durex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ravanson
- Niet gecategoriseerd AeroCool
- Niet gecategoriseerd QUIO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vantage Point
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jokari
- Niet gecategoriseerd BeeSecure
- Niet gecategoriseerd MantelMount
- Niet gecategoriseerd Unicol
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lasita Maja
- Niet gecategoriseerd Meccano
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oatey
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gretsch Guitars
- Niet gecategoriseerd Banoch
- Niet gecategoriseerd XP-PEN
- Niet gecategoriseerd Atmotube
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sun Pumps
- Niet gecategoriseerd Electrify
- Niet gecategoriseerd Leatt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bleep Labs
- Niet gecategoriseerd FontaFit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gossmann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Comatec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beringer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Atech Flash Technology
- Niet gecategoriseerd AutoParkTime
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ernitec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Facal
- Niet gecategoriseerd Planet Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Datacolor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Silicon Power
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sabrent
- Niet gecategoriseerd JAXY
- Niet gecategoriseerd WARN
- Niet gecategoriseerd TikkTokk
- Niet gecategoriseerd Roco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wibrain
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rolly Toys
- Niet gecategoriseerd Deditec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Level Mount
- Niet gecategoriseerd Teenage Engineering
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elipson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Create
- Niet gecategoriseerd STANDIVARIUS
- Niet gecategoriseerd CommScope
- Niet gecategoriseerd Videotec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Extralife Instruments
- Niet gecategoriseerd Genki Instruments
- Niet gecategoriseerd Industrial Music Electronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mauser Sitzkultur
- Niet gecategoriseerd Accezz
- Niet gecategoriseerd A4 Tech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zedar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yli Electronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dals
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bulman
- Niet gecategoriseerd TOOLMATE
- Niet gecategoriseerd SleepPro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Muama
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lepu Medical
- Niet gecategoriseerd Michigan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Waterdrop
- Niet gecategoriseerd ZCover
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vasagle
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lewitt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aquatica
- Niet gecategoriseerd Girmi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Goaliath
- Niet gecategoriseerd 909 Outdoor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Viomi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grimm Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kahayan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Better Life
- Niet gecategoriseerd TK Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dayclocks
- Niet gecategoriseerd Phidgets
- Niet gecategoriseerd Postium
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hawk-Woods
- Niet gecategoriseerd Novo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Commercial Chef
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dexibell
- Niet gecategoriseerd IsoAcoustics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Memphis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Clifford
- Niet gecategoriseerd AVMATRIX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cambo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hedbox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Adviti
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maclean
- Niet gecategoriseerd 9.solutions
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grundfos
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hotone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trace Elliot
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lockwood
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kospel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nexera
- Niet gecategoriseerd BlueDri
- Niet gecategoriseerd Seenergy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Meinl
- Niet gecategoriseerd Analogis
- Niet gecategoriseerd BBQ Premium
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stäubli
- Niet gecategoriseerd RAB
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schabus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eoslift
- Niet gecategoriseerd Steelton
- Niet gecategoriseerd FeinTech
- Niet gecategoriseerd BioChef
- Niet gecategoriseerd T-Rex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Waterco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Koolatron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kindercraft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tot Tutors
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tonar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Peterson
- Niet gecategoriseerd CFH
- Niet gecategoriseerd BOB Gear
- Niet gecategoriseerd Emeril Everyday
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rockboard
- Niet gecategoriseerd Goodis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nivian
- Niet gecategoriseerd L.R.Baggs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Millennia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vermona Modular
- Niet gecategoriseerd Adventure Kings
- Niet gecategoriseerd Drive Medical
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hitron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bliss Hammocks
- Niet gecategoriseerd Singular Sound
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maneco Labs
- Niet gecategoriseerd BISWIND
- Niet gecategoriseerd ABE Arnhold
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mermade Hair
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hover-1
- Niet gecategoriseerd Auer Signal
- Niet gecategoriseerd HELGI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Forge Adour
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eliminator Lighting
- Niet gecategoriseerd Darkglass
- Niet gecategoriseerd Paasche
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vistus
- Niet gecategoriseerd GMW
- Niet gecategoriseerd AER
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dynavox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Columbus
- Niet gecategoriseerd IWH
- Niet gecategoriseerd UGo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Code Mercenaries
- Niet gecategoriseerd SoundMagic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Diamex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sunset
- Niet gecategoriseerd IPEGA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Avital
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ondis24
- Niet gecategoriseerd D'Addario
- Niet gecategoriseerd BBE
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lemair
- Niet gecategoriseerd Warwick
- Niet gecategoriseerd MyAVR
- Niet gecategoriseerd EBS
- Niet gecategoriseerd WEICON
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rotronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Edsyn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Urban Glide
- Niet gecategoriseerd EISL
- Niet gecategoriseerd RCS
- Niet gecategoriseerd ARC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nicai Systems
- Niet gecategoriseerd IDENTsmart
- Niet gecategoriseerd Altrad
- Niet gecategoriseerd Revier Manager
- Niet gecategoriseerd Homak
- Niet gecategoriseerd Statron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tycon Systems
- Niet gecategoriseerd Selve
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lumel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Paingone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Howard Leight
- Niet gecategoriseerd Martens
- Niet gecategoriseerd Palmako
- Niet gecategoriseerd Desview
- Niet gecategoriseerd ActiveJet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Global Water
- Niet gecategoriseerd Allsee
- Niet gecategoriseerd Softing
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pulse ShowerSpas
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alogic
- Niet gecategoriseerd GFB
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sonicsmith
- Niet gecategoriseerd Toraiz
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ergodyne
- Niet gecategoriseerd Maturmeat
- Niet gecategoriseerd Orbsmart
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eowave
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nature2
- Niet gecategoriseerd AMERRY
- Niet gecategoriseerd ShelterLogic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Varad
- Niet gecategoriseerd UDG Gear
- Niet gecategoriseerd KMA Machines
- Niet gecategoriseerd CEDAR
- Niet gecategoriseerd Klark Teknik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Source Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd AtomoSynth
- Niet gecategoriseerd Benidub
- Niet gecategoriseerd Winston
- Niet gecategoriseerd Solidsteel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lectrosonics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dracast
- Niet gecategoriseerd Malouf
- Niet gecategoriseerd PureTools
- Niet gecategoriseerd SiriusXM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Earthwise
- Niet gecategoriseerd Raya
- Niet gecategoriseerd NANO Modules
- Niet gecategoriseerd Artex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Verbos Electronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ark
- Niet gecategoriseerd DLO
- Niet gecategoriseerd ENS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Listen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pentair
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oscium
- Niet gecategoriseerd Benchmark USA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Littelfuse
- Niet gecategoriseerd Game Factor
- Niet gecategoriseerd NComputing
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aguilar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brändi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mode Machines
- Niet gecategoriseerd Legends
- Niet gecategoriseerd AS Synthesizers
- Niet gecategoriseerd Itechworld
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nexcom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Janitza
- Niet gecategoriseerd SatKing
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fulltone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Advantix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wampler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hosa
- Niet gecategoriseerd VAEMI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Narva
- Niet gecategoriseerd DOK
- Niet gecategoriseerd OzCharge
- Niet gecategoriseerd MIYO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cioks
- Niet gecategoriseerd Neopower
- Niet gecategoriseerd AvMap
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arlec
- Niet gecategoriseerd REDARC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Guardian
- Niet gecategoriseerd Radio Flyer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gaslock
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gaffgun
- Niet gecategoriseerd AquaMAX
- Niet gecategoriseerd DigitSole
- Niet gecategoriseerd Portsmith
- Niet gecategoriseerd Flame
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rome
- Niet gecategoriseerd DW
- Niet gecategoriseerd BEA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Disty
- Niet gecategoriseerd OXI Instruments
- Niet gecategoriseerd AvaTime
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xhose
- Niet gecategoriseerd MYVU
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kopykake
- Niet gecategoriseerd Konstant Lab
- Niet gecategoriseerd Turbo Scrub
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tenderfoot Electronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kask
- Niet gecategoriseerd Callpod
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dorman
- Niet gecategoriseerd 2box
- Niet gecategoriseerd Enlight
- Niet gecategoriseerd Franken
- Niet gecategoriseerd RUBI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Europa Leisure
- Niet gecategoriseerd GAMO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Musser
- Niet gecategoriseerd Edge Products
- Niet gecategoriseerd IClever
- Niet gecategoriseerd HN-Power
- Niet gecategoriseerd BIONIK
- Niet gecategoriseerd King Canopy
- Niet gecategoriseerd HeadRush
- Niet gecategoriseerd ChamSys
- Niet gecategoriseerd Milestone Systems
- Niet gecategoriseerd Flover
- Niet gecategoriseerd Micsig
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dodow
- Niet gecategoriseerd Spring
- Niet gecategoriseerd Red Panda
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aquasure
- Niet gecategoriseerd Banana Pi
- Niet gecategoriseerd American International
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crazy Tube Circuits
- Niet gecategoriseerd J.P. Instruments
- Niet gecategoriseerd GMB Gaming
- Niet gecategoriseerd Proclip
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kaona
- Niet gecategoriseerd Baja Mobility
- Niet gecategoriseerd DPW Design
- Niet gecategoriseerd SinuPulse
- Niet gecategoriseerd The T.bone
- Niet gecategoriseerd DIEZEL
- Niet gecategoriseerd VMB
- Niet gecategoriseerd Z.Vex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Seymour Duncan
- Niet gecategoriseerd BluGuitar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lehle
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bricasti Design
- Niet gecategoriseerd T.akustik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dwarf Connection
- Niet gecategoriseerd JL Cooper
- Niet gecategoriseerd StrikeMaster
- Niet gecategoriseerd ProUser
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bēm Wireless
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aqua-Vu
- Niet gecategoriseerd Millecroquettes
- Niet gecategoriseerd GR Bass
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sure-Fi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gumdrop
- Niet gecategoriseerd Copernicus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tellur
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gallien-Krueger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jetway
- Niet gecategoriseerd Texsport
- Niet gecategoriseerd SSV Works
- Niet gecategoriseerd Terre
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sanitec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pangea Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hogue
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pfannenberg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Scytek
- Niet gecategoriseerd MotorScrubber
- Niet gecategoriseerd Krone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kraftmax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Steelplay
- Niet gecategoriseerd PCTV Systems
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cooper Lighting
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sound Devices
- Niet gecategoriseerd Code Corporation
- Niet gecategoriseerd Now TV
- Niet gecategoriseerd Promise Technology
- Niet gecategoriseerd Voodoo Lab
- Niet gecategoriseerd Strymon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Insect Lore
- Niet gecategoriseerd FSR
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chrome-Q
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kitronik
- Niet gecategoriseerd SumUp
- Niet gecategoriseerd Microlab
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rotolight
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lumu
- Niet gecategoriseerd Salicru
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vankyo
- Niet gecategoriseerd WAYDOO
- Niet gecategoriseerd ASIWO
- Niet gecategoriseerd OWC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vent-Axia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Firefield
- Niet gecategoriseerd E-Power
- Niet gecategoriseerd RectorSeal
- Niet gecategoriseerd Red Digital Cinema
- Niet gecategoriseerd Marathon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kaiser Nienhaus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Freeplay
- Niet gecategoriseerd Roller Grill
- Niet gecategoriseerd DCS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zaor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Glorious
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cleco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dataflex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Handy Lux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rossum Electro-Music
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pentel
- Niet gecategoriseerd MagnaPool
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aquadon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Raidsonic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gamesir
- Niet gecategoriseerd Neunaber
- Niet gecategoriseerd ENDORFY
- Niet gecategoriseerd DPM
- Niet gecategoriseerd VOREL
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ciarra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ocean Way Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd DayStar Filters
- Niet gecategoriseerd OP/TECH
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alfatron
- Niet gecategoriseerd ETC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vertex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nuki
- Niet gecategoriseerd SWIT
- Niet gecategoriseerd EOTech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zacuto
- Niet gecategoriseerd Key Digital
- Niet gecategoriseerd TVLogic
- Niet gecategoriseerd CAD Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Feelworld
- Niet gecategoriseerd Frequency Central
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sacrament
- Niet gecategoriseerd The Box
- Niet gecategoriseerd SoundPEATS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cambium Networks
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trident
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schoeps
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tilta
- Niet gecategoriseerd HPI Racing
- Niet gecategoriseerd COLBOR
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trijicon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Favini
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dnipro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dot Line
- Niet gecategoriseerd KJB Security Products
- Niet gecategoriseerd Polsen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Whirlwind
- Niet gecategoriseerd IFootage
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gen Energy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Saint Algue
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cactus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oecolux
- Niet gecategoriseerd Core SWX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Multibrackets
- Niet gecategoriseerd SoundLAB
- Niet gecategoriseerd ACL
- Niet gecategoriseerd SurgeX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Einhell Bavaria
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mars Gaming
- Niet gecategoriseerd G.Skill
- Niet gecategoriseerd Edbak
- Niet gecategoriseerd Integral LED
- Niet gecategoriseerd Integral
- Niet gecategoriseerd Roline
- Niet gecategoriseerd Virax
- Niet gecategoriseerd SAVS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sightron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mount-It!
- Niet gecategoriseerd Uniropa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Proviel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Amaran
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gill
- Niet gecategoriseerd Triangle
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tumbleweed
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alutruss
- Niet gecategoriseerd Omega Altise
- Niet gecategoriseerd PVI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Avenview
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grendel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Coravin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Weidmüller
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mac Tools
- Niet gecategoriseerd BSS Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd O&O Software
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wasp
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chef's Choice
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ciclo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brastemp
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wavtech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Satco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Buxton
- Niet gecategoriseerd AMT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sabco
- Niet gecategoriseerd MAK
- Niet gecategoriseerd CELLFAST
- Niet gecategoriseerd Flo
- Niet gecategoriseerd CLIMAQUA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lowell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Adonit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Point Source Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd ANDYCINE
- Niet gecategoriseerd AmpliVox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Moomin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pippi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Memphis Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Casalux
- Niet gecategoriseerd CyberData Systems
- Niet gecategoriseerd Omnitron Systems
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stewart Systems
- Niet gecategoriseerd SwitchBot
- Niet gecategoriseerd Qubino
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eurosound
- Niet gecategoriseerd BZBGear
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rolls
- Niet gecategoriseerd WyreStorm
- Niet gecategoriseerd K&M
- Niet gecategoriseerd Williams Sound
- Niet gecategoriseerd Magewell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rocstor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Globalo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Adam Hall
- Niet gecategoriseerd SoundTube
- Niet gecategoriseerd Flaem
- Niet gecategoriseerd Therabody
- Niet gecategoriseerd Infortrend
- Niet gecategoriseerd STI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rug Doctor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mad Dog
- Niet gecategoriseerd Raspberry Pi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bals
- Niet gecategoriseerd Balt
- Niet gecategoriseerd Perixx
- Niet gecategoriseerd AJ.BA
- Niet gecategoriseerd ESKA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lascar Electronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd EWON
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sport-Tronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alga
- Niet gecategoriseerd WesAudio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Heritage Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Quik Lok
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tsakalis AudioWorks
- Niet gecategoriseerd Venus
- Niet gecategoriseerd MagTek
- Niet gecategoriseerd SmallRig
- Niet gecategoriseerd Drake
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sony Optiarc
- Niet gecategoriseerd Colortone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lowel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Anybus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Super Rod
- Niet gecategoriseerd Luminex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Epiphan
- Niet gecategoriseerd HiLook
- Niet gecategoriseerd Deltaco Gaming
- Niet gecategoriseerd P3 International
- Niet gecategoriseerd Idec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beckmann & Egle
- Niet gecategoriseerd Seek Thermal
- Niet gecategoriseerd VintageView
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alfresco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bintec-elmeg
- Niet gecategoriseerd W'eau
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ixxat
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fanox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crouzet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Megarevo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tech 21
- Niet gecategoriseerd BlendMount
- Niet gecategoriseerd Perlick
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sedona
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tecnoinox
- Niet gecategoriseerd CaterRacks
- Niet gecategoriseerd Besco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Scotsman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Atosa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nanoleaf
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mach Power
- Niet gecategoriseerd Soltection
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kool-It
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cool Head
- Niet gecategoriseerd LawnMaster
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eligent
- Niet gecategoriseerd Meris
- Niet gecategoriseerd Procare
- Niet gecategoriseerd AmerBox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Qu-Bit
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blue Lantern
- Niet gecategoriseerd DivKid
- Niet gecategoriseerd Uniross
- Niet gecategoriseerd Panamax
- Niet gecategoriseerd FaseLunare
- Niet gecategoriseerd Götze & Jensen
- Niet gecategoriseerd (Recovery)
- Niet gecategoriseerd Twinkly
- Niet gecategoriseerd Acefast
- Niet gecategoriseerd Squarp Instruments
- Niet gecategoriseerd EtherWAN
- Niet gecategoriseerd Econ Connect
- Niet gecategoriseerd META
- Niet gecategoriseerd Shimbol
- Niet gecategoriseerd GC Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Motrona
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thalheimer
- Niet gecategoriseerd AkYtec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ergotools Pattfield
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lynx Technik
- Niet gecategoriseerd FeiYu-Tech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Apantac
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ambient Weather
- Niet gecategoriseerd VisionTek
- Niet gecategoriseerd MuxLab
- Niet gecategoriseerd EMeet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Accsoon
- Niet gecategoriseerd FeiyuTech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bessey
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ledvance
- Niet gecategoriseerd Serge
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gladiator
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nyko
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mobli
- Niet gecategoriseerd StarIink
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sonoff
- Niet gecategoriseerd Caroma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Befaco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Waltec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eartec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elvid
- Niet gecategoriseerd ORCA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Portkeys
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nextorage
- Niet gecategoriseerd Freewell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Westcott
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sky-Watcher
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tempo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Evolis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Digiquest
- Niet gecategoriseerd EXSYS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gewiss
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hagor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Glyph
- Niet gecategoriseerd Envitec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Murr Elektronik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Camille Bauer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Seco-Larm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Massoth
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cropico
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mimo Monitors
- Niet gecategoriseerd Alula
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blebox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Redsbaby
- Niet gecategoriseerd Seaward
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bright Spark
- Niet gecategoriseerd Algo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gentrax
- Niet gecategoriseerd ICC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gamber-Johnson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Insteon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brocade
- Niet gecategoriseerd Altronix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Amer
- Niet gecategoriseerd Longvie
- Niet gecategoriseerd Coca-Cola
- Niet gecategoriseerd Warner Bros
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vinotemp
- Niet gecategoriseerd Silent Knight
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mosconi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ditek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stelzner
- Niet gecategoriseerd Axxess
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wilson
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kingston Technology
- Niet gecategoriseerd Goki
- Niet gecategoriseerd My Arcade
- Niet gecategoriseerd Enttec
- Niet gecategoriseerd RF Elements
- Niet gecategoriseerd ALC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Triumph Sports
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elbro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Holland Electronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arista
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chenbro Micom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crelando
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ionmax
- Niet gecategoriseerd DeepCool
- Niet gecategoriseerd TechLogix Networx
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thermalright
- Niet gecategoriseerd EchoMaster
- Niet gecategoriseerd PS Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Meross
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lively
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bxterra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bea-fon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Renogy
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ordo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Biostar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Asetek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Audibax
- Niet gecategoriseerd TechN
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eversolo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Giga Copper
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elsner
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cube Controls
- Niet gecategoriseerd Donexon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eve Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Axagon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Linq
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wortmann AG
- Niet gecategoriseerd DiGiGrid
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mitzu
- Niet gecategoriseerd Avteq
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fizzics
- Niet gecategoriseerd XFX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Leynew
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lauten Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sunwoda
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schleich
- Niet gecategoriseerd Unitech
- Niet gecategoriseerd FXLab
- Niet gecategoriseerd Middle Atlantic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kincrome
- Niet gecategoriseerd BC Acoustique
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brockhaus HEUER
- Niet gecategoriseerd Reishunger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ergotec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dupla
- Niet gecategoriseerd APSystems
- Niet gecategoriseerd IODD
- Niet gecategoriseerd BYD
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tektronix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aqua Medic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gold Note
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pylontech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fire Sense
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grüniq
- Niet gecategoriseerd Goodwe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Moki
- Niet gecategoriseerd Enertex
- Niet gecategoriseerd IOTAVX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Creality
- Niet gecategoriseerd OM SYSTEM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ovation
- Niet gecategoriseerd InAlto
- Niet gecategoriseerd MDT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Enviroswim
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vevor
- Niet gecategoriseerd PowerColor
- Niet gecategoriseerd ISpring
- Niet gecategoriseerd WeFix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Serpent
- Niet gecategoriseerd Saki
- Niet gecategoriseerd Smart365
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fosi Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd ChargeHub
- Niet gecategoriseerd PUR
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eldat
- Niet gecategoriseerd NEP
- Niet gecategoriseerd SoundSwitch
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sera
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dostmann Electronic
- Niet gecategoriseerd A-NeuVideo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Murideo
- Niet gecategoriseerd ToughTested
- Niet gecategoriseerd JBC
- Niet gecategoriseerd DV Mark
- Niet gecategoriseerd MOON
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cuggl
- Niet gecategoriseerd HABAU
- Niet gecategoriseerd CVW
- Niet gecategoriseerd Majority
- Niet gecategoriseerd Earbreeze
- Niet gecategoriseerd S.M.S.L
- Niet gecategoriseerd Möhlenhoff
- Niet gecategoriseerd Taqua
- Niet gecategoriseerd NightStick
- Niet gecategoriseerd IBEAM
- Niet gecategoriseerd ChyTV
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brainstorm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Colonial Elegance
- Niet gecategoriseerd Overtone Labs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bühnen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blukac
- Niet gecategoriseerd BendixKing
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tube-Tech
- Niet gecategoriseerd TCW Technologies
- Niet gecategoriseerd UNITEK
- Niet gecategoriseerd CoolerMaster
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rexing
- Niet gecategoriseerd NuPrime
- Niet gecategoriseerd The T.mix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Regula-Werk King
- Niet gecategoriseerd Inter-M
- Niet gecategoriseerd MIDI Solutions
- Niet gecategoriseerd Positive Grid
- Niet gecategoriseerd Amgrow
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xaphoon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Winchester
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lampa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sinus Live
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sureguard
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dobot
- Niet gecategoriseerd QuickCool
- Niet gecategoriseerd Smit Visual
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oro-Med
- Niet gecategoriseerd NZR
- Niet gecategoriseerd Toparc
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Baby Cakes
- Niet gecategoriseerd Deflecto
- Niet gecategoriseerd ELMEKO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tesseract Modular
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sport Dog
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nowsonic
- Niet gecategoriseerd On Air
- Niet gecategoriseerd E-ast
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hubble Connected
- Niet gecategoriseerd ELTA Music
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oliveri
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dragonshock
- Niet gecategoriseerd We-Vibe
- Niet gecategoriseerd Envertech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Budda
- Niet gecategoriseerd Electronics International
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lamar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Atlantis Land
- Niet gecategoriseerd White Lightning
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hoymiles
- Niet gecategoriseerd Deye
- Niet gecategoriseerd My Wall
- Niet gecategoriseerd Frient
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kaiser Fototechnik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vishay
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sonorous
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rooboost
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bitspower
- Niet gecategoriseerd JMAZ Lighting
- Niet gecategoriseerd EAT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Comar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Freedor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Start International
- Niet gecategoriseerd C2G
- Niet gecategoriseerd AXITEC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lingg & Janke
- Niet gecategoriseerd Auralex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Innovative
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yuede
- Niet gecategoriseerd ClimeMET
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pliant Technologies
- Niet gecategoriseerd Prompter People
- Niet gecategoriseerd Astropet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Busch + Müller
- Niet gecategoriseerd Canopia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wabeco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Swingline GBC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Spelsberg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Staudte-Hirsch
- Niet gecategoriseerd Soundsphere
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lantronix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kino Flo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aqua Computer
- Niet gecategoriseerd HEDD
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vinpower Digital
- Niet gecategoriseerd Magivaac
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lindemann
- Niet gecategoriseerd Silent Angel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bavaria By Einhell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Healthy Choice
- Niet gecategoriseerd IOptron
- Niet gecategoriseerd ZWO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bbf
- Niet gecategoriseerd Club 3D
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sprolink
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thermionic Culture
- Niet gecategoriseerd BMB
- Niet gecategoriseerd Watercool
- Niet gecategoriseerd Moultrie
- Niet gecategoriseerd Skaarhoj
- Niet gecategoriseerd Microboards
- Niet gecategoriseerd Whitestone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Advance
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arylic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gem Toys
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cloud
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sandia Aerospace
- Niet gecategoriseerd EK Water Blocks
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lamptron
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gudsen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Café
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zendure
- Niet gecategoriseerd Phanteks
- Niet gecategoriseerd Prism Sound
- Niet gecategoriseerd MoFi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gosund
- Niet gecategoriseerd Artecta
- Niet gecategoriseerd DMT
- Niet gecategoriseerd FSP/Fortron
- Niet gecategoriseerd IDIS
- Niet gecategoriseerd CM Storm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Meopta
- Niet gecategoriseerd MARTOR
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lumantek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Transparent
- Niet gecategoriseerd Audiotec Fischer
- Niet gecategoriseerd SEADA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Deity
- Niet gecategoriseerd Taga Harmony
- Niet gecategoriseerd B.E.G.
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fixpoint
- Niet gecategoriseerd Enerdrive
- Niet gecategoriseerd TESLA Electronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Intesis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nethix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pluto
- Niet gecategoriseerd Laine
- Niet gecategoriseerd 3Doodler
- Niet gecategoriseerd Soundskins
- Niet gecategoriseerd Middle Atlantic Products
- Niet gecategoriseerd Doepke
- Niet gecategoriseerd Loctite
- Niet gecategoriseerd Datapath
- Niet gecategoriseerd Antelope
- Niet gecategoriseerd Astera
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vertiv
- Niet gecategoriseerd Polyend
- Niet gecategoriseerd BASSBOSS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sensative
- Niet gecategoriseerd Plasma Cloud
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sheeran Looper
- Niet gecategoriseerd Applico
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jungle Gym
- Niet gecategoriseerd Smart Media
- Niet gecategoriseerd BLUEPALM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hacienda
- Niet gecategoriseerd Christmaxx
- Niet gecategoriseerd IStarUSA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Code
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mivar
- Niet gecategoriseerd SolaX Power
- Niet gecategoriseerd IPGARD
- Niet gecategoriseerd EZ Dupe
- Niet gecategoriseerd AURALiC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Qian
- Niet gecategoriseerd Revic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Absco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schatten Design
- Niet gecategoriseerd LEDs-ON
- Niet gecategoriseerd WiiM
- Niet gecategoriseerd MyPOS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Truetone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stages
- Niet gecategoriseerd Starlink
- Niet gecategoriseerd HDFury
- Niet gecategoriseerd Favero
- Niet gecategoriseerd Durvet
- Niet gecategoriseerd MAAS
- Niet gecategoriseerd KNEKT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gator Frameworks
- Niet gecategoriseerd Storm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Teia
- Niet gecategoriseerd The Joy Factory
- Niet gecategoriseerd API Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Axor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yuer
- Niet gecategoriseerd OSEE
- Niet gecategoriseerd OLLO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gustard
- Niet gecategoriseerd Enhance
- Niet gecategoriseerd MEPROLIGHT
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tactical Fiber Systems
- Niet gecategoriseerd GVision
- Niet gecategoriseerd Veber
- Niet gecategoriseerd PurAthletics
- Niet gecategoriseerd SMS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Carlo Gavazzi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Richgro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Varaluz
- Niet gecategoriseerd Milesight
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dehner
- Niet gecategoriseerd Edwards
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cotek
- Niet gecategoriseerd Victor Technology
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lastolite
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lowepro
- Niet gecategoriseerd MIOPS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Grand Effects
- Niet gecategoriseerd EA Elektro Automatik
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hensel
- Niet gecategoriseerd Westland
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bahr
- Niet gecategoriseerd Black Line
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sodapop
- Niet gecategoriseerd Enbrighten
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vicoustic
- Niet gecategoriseerd TAURUS Titanium
- Niet gecategoriseerd Magliner
- Niet gecategoriseerd Magmatic
- Niet gecategoriseerd PulseAudio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cayin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Comfortisse
- Niet gecategoriseerd Videotel Digital
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zylight
- Niet gecategoriseerd Smith-Victor
- Niet gecategoriseerd HuddleCamHD
- Niet gecategoriseerd Technical Pro
- Niet gecategoriseerd MooreCo
- Niet gecategoriseerd BIOS Living
- Niet gecategoriseerd Connection
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blind Spot
- Niet gecategoriseerd Badiona
- Niet gecategoriseerd VMV
- Niet gecategoriseerd Digigram
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mutec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Black Hydra
- Niet gecategoriseerd Expressive E
- Niet gecategoriseerd Merging
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bellari
- Niet gecategoriseerd FoxFury
- Niet gecategoriseerd Altman
- Niet gecategoriseerd EXO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hawke
- Niet gecategoriseerd Betty Bossi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eller
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rotatrim
- Niet gecategoriseerd Claypaky
- Niet gecategoriseerd Peak Design
- Niet gecategoriseerd Eura
- Niet gecategoriseerd ESE
- Niet gecategoriseerd Casa Deco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hecate
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jinbei
- Niet gecategoriseerd Christmas Time
- Niet gecategoriseerd Comprehensive
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nearity
- Niet gecategoriseerd Easyrig
- Niet gecategoriseerd Digitalinx
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gra-Vue
- Niet gecategoriseerd WHD
- Niet gecategoriseerd On-Stage
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sumiko
- Niet gecategoriseerd Indiana Line
- Niet gecategoriseerd TechBite
- Niet gecategoriseerd Inverx
- Niet gecategoriseerd Primewire
- Niet gecategoriseerd XCell
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yellow Garden Line
- Niet gecategoriseerd Titanwolf
- Niet gecategoriseerd Uplink
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mybeo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Medicinalis
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bearware
- Niet gecategoriseerd Liam&Daan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Traco Power
- Niet gecategoriseerd Microair
- Niet gecategoriseerd Perfect Christmas
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bebob
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fiilex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Analog Way
- Niet gecategoriseerd PTZ Optics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sescom
- Niet gecategoriseerd Robus
- Niet gecategoriseerd DEERSYNC
- Niet gecategoriseerd CAME-TV
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rosco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wimberley
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nureva
- Niet gecategoriseerd Telmax
- Niet gecategoriseerd Apollo Design
- Niet gecategoriseerd JoeCo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Holosun
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aconatic
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kluge
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arovec
- Niet gecategoriseerd SecureSafe
- Niet gecategoriseerd CubuSynth
- Niet gecategoriseerd Exelpet
- Niet gecategoriseerd Imarflex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tempmate
- Niet gecategoriseerd Carlsbro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ventev
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mobotix
- Niet gecategoriseerd UNYKAch
- Niet gecategoriseerd VAVA
- Niet gecategoriseerd Modbap Modular
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bluestork
- Niet gecategoriseerd INOGENI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Linhof
- Niet gecategoriseerd Carry-on
- Niet gecategoriseerd AddLiving
- Niet gecategoriseerd IOIO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nimbus
- Niet gecategoriseerd LiveU
- Niet gecategoriseerd City Theatrical
- Niet gecategoriseerd Redback Technologies
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vent-A-Hood
- Niet gecategoriseerd GoXtreme
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bome
- Niet gecategoriseerd One Control
- Niet gecategoriseerd EQ Acoustics
- Niet gecategoriseerd AV Tool
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aquael
- Niet gecategoriseerd NEXTO DI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Thermarest
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fortinge
- Niet gecategoriseerd RF-Links
- Niet gecategoriseerd Y-brush
- Niet gecategoriseerd Austral
- Niet gecategoriseerd HMD
- Niet gecategoriseerd Luxul
- Niet gecategoriseerd Brizo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cherub
- Niet gecategoriseerd Huslog
- Niet gecategoriseerd ProLights
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xinfrared
- Niet gecategoriseerd I-PRO
- Niet gecategoriseerd Europalms
- Niet gecategoriseerd DuroStar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Waterstone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mr Steam
- Niet gecategoriseerd WarmlyYours
- Niet gecategoriseerd DVDO
- Niet gecategoriseerd A-Designs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Henry Engineering
- Niet gecategoriseerd Primacoustic
- Niet gecategoriseerd HomeCraft
- Niet gecategoriseerd Heusinkveld
- Niet gecategoriseerd EnOcean
- Niet gecategoriseerd Storcube
- Niet gecategoriseerd Robern
- Niet gecategoriseerd Noyafa
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gurari
- Niet gecategoriseerd Varia
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fezz
- Niet gecategoriseerd ASI
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lexivon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Graff
- Niet gecategoriseerd Swiss Eye
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cane Creek
- Niet gecategoriseerd EPEVER
- Niet gecategoriseerd KED
- Niet gecategoriseerd Exped
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lawn Star
- Niet gecategoriseerd Edouard Rousseau
- Niet gecategoriseerd GameDay
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sparkle
- Niet gecategoriseerd Söll
- Niet gecategoriseerd X-Lite
- Niet gecategoriseerd AXESS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Glemm
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ridem
- Niet gecategoriseerd Belanger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Røde
- Niet gecategoriseerd Envertec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Volcano
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nordic Winter
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wire Technologies
- Niet gecategoriseerd Taco Tuesday
- Niet gecategoriseerd CEEM
- Niet gecategoriseerd IMM Photonics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Field Optics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Signature Hardware
- Niet gecategoriseerd UAvionix
- Niet gecategoriseerd Roesle
- Niet gecategoriseerd GRAUGEAR
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sure Petcare
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sortimo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beaphar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Mebby
- Niet gecategoriseerd TONI&GUY
- Niet gecategoriseerd Balam Rush
- Niet gecategoriseerd Oreg
- Niet gecategoriseerd Karran
- Niet gecategoriseerd Topex
- Niet gecategoriseerd OOONO
- Niet gecategoriseerd CaviLock
- Niet gecategoriseerd Origin Storage
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kostal
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stamos
- Niet gecategoriseerd Stamony
- Niet gecategoriseerd Yamazen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sharkbite
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pivo
- Niet gecategoriseerd YA-MAN
- Niet gecategoriseerd Taiji
- Niet gecategoriseerd LightKeeper Pro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Belulu
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hellberg
- Niet gecategoriseerd CRAFT + MAIN
- Niet gecategoriseerd V-Tone
- Niet gecategoriseerd Symmons
- Niet gecategoriseerd LARQ
- Niet gecategoriseerd Corona
- Niet gecategoriseerd Uvex
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dynon Avionics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Coors Light
- Niet gecategoriseerd KoolScapes
- Niet gecategoriseerd Arco
- Niet gecategoriseerd Venicci
- Niet gecategoriseerd Noordi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jedo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Dinstar
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bayco
- Niet gecategoriseerd RIX
- Niet gecategoriseerd Matterport
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nicols
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vitec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Das Keyboard
- Niet gecategoriseerd Schaffner
- Niet gecategoriseerd Platypus
- Niet gecategoriseerd Royale
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jacuzzi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gerber
- Niet gecategoriseerd NeoMounts
- Niet gecategoriseerd Klauke
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bulgin
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pure 100
- Niet gecategoriseerd Soler & Palau
- Niet gecategoriseerd STANDARD
- Niet gecategoriseerd RC Allen
- Niet gecategoriseerd Triplett
- Niet gecategoriseerd Wiesenfield
- Niet gecategoriseerd Plastkon
- Niet gecategoriseerd BigBlue
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tele Vue
- Niet gecategoriseerd Icron
- Niet gecategoriseerd AstrHori
- Niet gecategoriseerd Studio Titan
- Niet gecategoriseerd Petite Chérie
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sifflus
- Niet gecategoriseerd HPRC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crystal Video
- Niet gecategoriseerd Blonder Tongue
- Niet gecategoriseerd Luxli
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ferrofish
- Niet gecategoriseerd Really Right Stuff
- Niet gecategoriseerd PAG
- Niet gecategoriseerd ButtKicker
- Niet gecategoriseerd Decimator
- Niet gecategoriseerd Chimera
- Niet gecategoriseerd Trezor
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rohl
- Niet gecategoriseerd ProFlo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Western Co.
- Niet gecategoriseerd Senseca
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ruggard
- Niet gecategoriseerd Moman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Aalberg Audio
- Niet gecategoriseerd Violectric
- Niet gecategoriseerd DiversiTech
- Niet gecategoriseerd Evooch
- Niet gecategoriseerd Total Chef
- Niet gecategoriseerd Bolin Technology
- Niet gecategoriseerd PoLabs
- Niet gecategoriseerd Digi-Pas
- Niet gecategoriseerd Fellow
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pfister
- Niet gecategoriseerd Axler
- Niet gecategoriseerd ARNOLD Lichttechnik
- Niet gecategoriseerd BMAX
- Niet gecategoriseerd CatSynth
- Niet gecategoriseerd Ember
- Niet gecategoriseerd ACOPower
- Niet gecategoriseerd Vantrue
- Niet gecategoriseerd SafeMi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cosi Home
- Niet gecategoriseerd GeoBox
- Niet gecategoriseerd Telycam
- Niet gecategoriseerd URC
- Niet gecategoriseerd Advanced Network Devices
- Niet gecategoriseerd JLCooper
- Niet gecategoriseerd DQ
- Niet gecategoriseerd Rock N Roller
- Niet gecategoriseerd XTRARM
- Niet gecategoriseerd Twisted Electrons
- Niet gecategoriseerd ZZ-2
- Niet gecategoriseerd OptiTrack
- Niet gecategoriseerd Doona
- Niet gecategoriseerd USL
- Niet gecategoriseerd Induction Dynamics
- Niet gecategoriseerd SolidDrive
- Niet gecategoriseerd SKB
- Niet gecategoriseerd Cyber Acoustics
- Niet gecategoriseerd MSolutions
- Niet gecategoriseerd QZ
- Niet gecategoriseerd Helight
- Niet gecategoriseerd Boehringer Ingelheim
- Niet gecategoriseerd Singularity Computers
- Niet gecategoriseerd DARTS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Xuma
- Niet gecategoriseerd Go-eCharger
- Niet gecategoriseerd Autoscript
- Niet gecategoriseerd Digital Forecast
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sesame Street
- Niet gecategoriseerd InvisibleShield
- Niet gecategoriseerd SmartGyro
- Niet gecategoriseerd Gator
- Niet gecategoriseerd XD-Design
- Niet gecategoriseerd Star Belly
- Niet gecategoriseerd CkeyiN
- Niet gecategoriseerd Phase Technology
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hypnos
- Niet gecategoriseerd Casr
- Niet gecategoriseerd Louroe Electronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kaorka
- Niet gecategoriseerd Livn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zaahn
- Niet gecategoriseerd Orbitrek
- Niet gecategoriseerd BlaknBlu
- Niet gecategoriseerd Crem
- Niet gecategoriseerd MOOOV
- Niet gecategoriseerd Sportime
- Niet gecategoriseerd Tece
- Niet gecategoriseerd Zeapon
- Niet gecategoriseerd Quasar Science
- Niet gecategoriseerd Beltronics
- Niet gecategoriseerd Jan Nowak
- Niet gecategoriseerd Lahti Pro
- Niet gecategoriseerd HiRO
- Niet gecategoriseerd MOZOS
- Niet gecategoriseerd Forodi
- Niet gecategoriseerd Elight
- Niet gecategoriseerd ViewZ
- Niet gecategoriseerd IsoTek
- Niet gecategoriseerd VARI-LITE
- Niet gecategoriseerd Real Cable
- Niet gecategoriseerd Miracle Smile
- Niet gecategoriseerd Pengo
- Niet gecategoriseerd Racktime
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kica
- Niet gecategoriseerd Starlight Xpress
- Niet gecategoriseerd Kendall Howard
- Niet gecategoriseerd Leba
- Niet gecategoriseerd Infosec
- Niet gecategoriseerd Simmons
- Niet gecategoriseerd Therm-a-Rest
- Niet gecategoriseerd Hoffman
- Niet gecategoriseerd Nofred
- Niet gecategoriseerd Diamond Audio
Nieuwste handleidingen voor Niet gecategoriseerd

9 April 2025

9 April 2025

9 April 2025

9 April 2025

9 April 2025

9 April 2025

9 April 2025

9 April 2025

9 April 2025

9 April 2025